Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
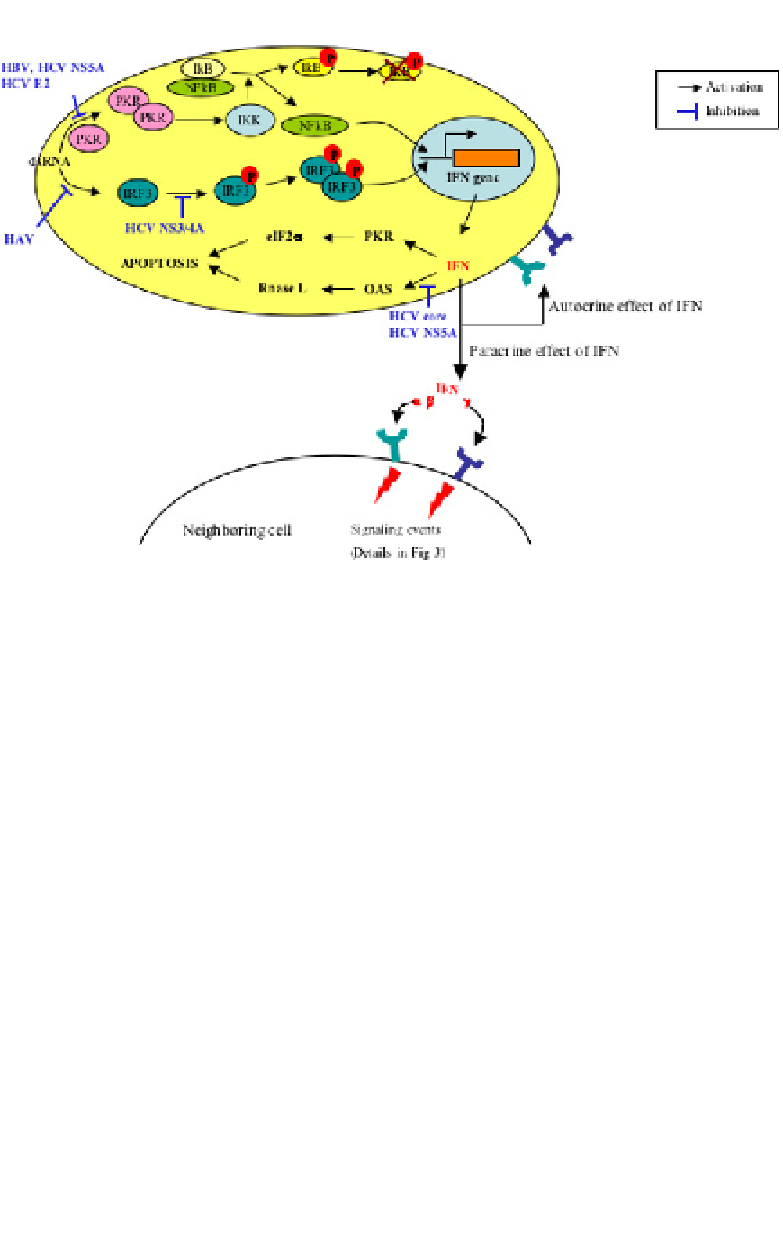
Fig. 2.
Interferon action and the effects of hepatitis viruses.
induce the transcriptional activation of at least 30 cellu-
lar genes of the cytokine family.
13
IFN
α
and
β
, is pro-
duced by natural killer (NK) cells and activated T lymphocytes in
response to viral infection. Several interferon-induced cellular pro-
teins have been implicated in its antiviral action within an infected
cell. These are a dsRNA-induced protein kinase (PKR),
14
Type II interferon, IFN
γ
-
oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS),
15
the RNA specific adenosine deam-
inase (ADAR),
16,17
and the Mx protein GTPases.
18
We will consider
the known effects of hepatitis viruses on each of these pathways sep-
arately. For the sake of clarity, we will divide the interferon system into
events that take place inside infected cells and those that result from
the action of interferons on uninfected neighboring cells (Fig. 2).
the 2
′
-5
′
Events in Virus-infected Cells
Most viruses produce double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) at some stage
of their replication cycle
12
and these are potent inducers of the IFN