Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
For many years, HAases have been used as a spreading factor. The HAase prepara-
tions are used as adjuvant to increase the absorption and dispersion of injected drugs
into the tissue ECM. On the basis of our results, we may suggest that efficiency of
such HAase preparations would strongly depend on the composition of the ECM of
the tissues where they are injected. Moreover, HAases are also used to prepare HA
fragments with well-defined sizes (Deschrevel, in press). We showed that with a HA
concentration of 5 g l
-
1
, at pH 4 and at 37°C, HA fragments of different ranges of mo-
lar masses can be produce by properly selecting the HAase concentration, the ionic
strength and the end reation time (Tranchepain et al., 2006). The HA fragments were
then purified by using size exclusion chromatography followed by dialysis for salt
elimination. More recently, we showed that BSA could be efficiently used instead of
salt to increase the rate of HA hydrolysis catalyzed by BT-HAase. Thereby, we were
able to enzymatically produce high quantities of HA tetrasaccharide within a rather
short reaction time and, above all, because the reaction mixture did not contain any
salt, purification could be rapidly and efficiently performed by using an ultra filtration
method (unpublished results).
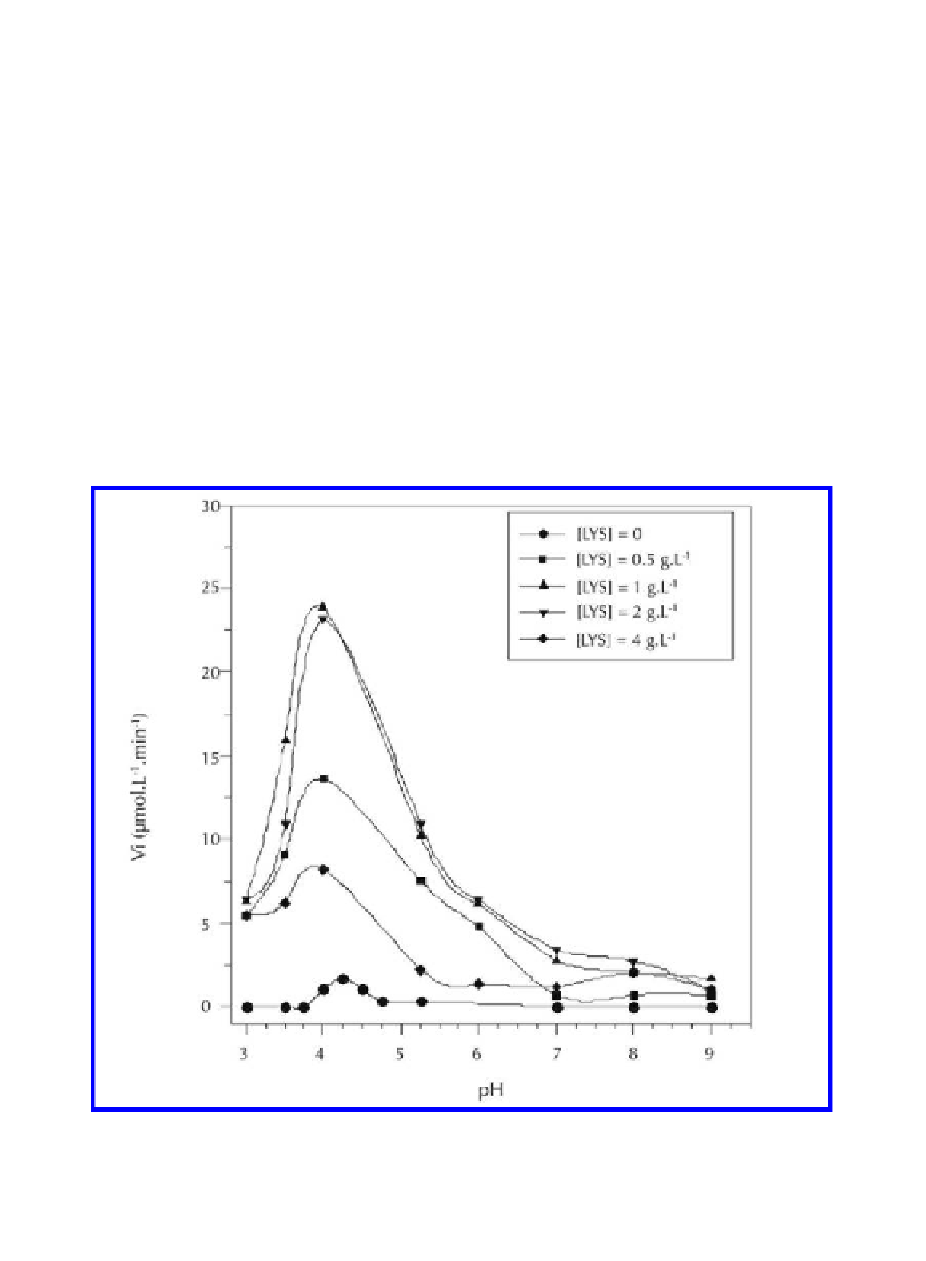
Figure 12.
pH-dependence of the HA hydrolysis catalyzed by BT-HAase in 5 mmol l
-1
sodium
chloride and at 37°C, for different LYS concentrations ranging from 0 to 4 g l
-1
. The HA concentration
was 1 g l
-1
and the BT-HAase concentration was 0.5 g l
-1
. The number average molar mass of HA was
0.97
×
10
6
g mol
-1
. Data from Lenormand et al. (2010a).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search