Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
HA and BT-HAase in which BT-HAase is catalytically inactive (Deschrevel et al.,
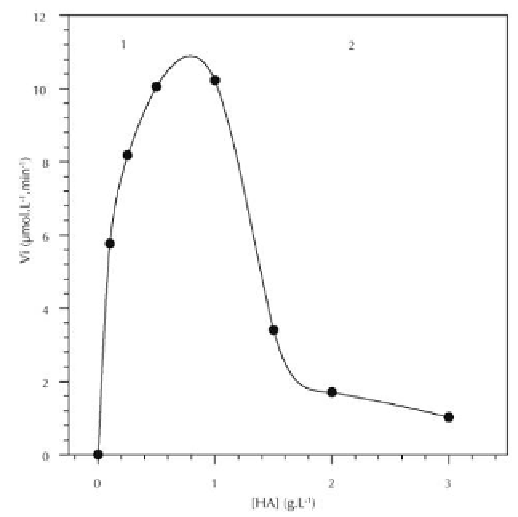
2008a). Let us see how this conclusion allows us to explain the atypical shape of the
substrate-dependence curves. When we studied the influence of the HA concentration
on the initial rate of HA enzymatic hydrolysis, we used a fixed BT-HAase concentra-
tion. However, when using experimental conditions under which BT-HAase formed
electrostatic complexes with HA, the higher the HA concentration, the higher the part
of BT-HAase involved in electrostatic complexes. But, since BT-HAase involved in
electrostatic complexes was catalytically inactive, increasing the HA concentration
also meant a decrease in the concentration of active BT-HAase. Thus, in the first part
of the substrate-dependence curve (Figure 5, part 1), the increase in the HA concentra-
tion enabled the initial hydrolysis rate to increase despite of the decrease in the con-
centration of active BT-HAase. On the contrary, in the second part of the curve (Figure
5, part 2), the increase in the HA concentration was no-longer sufficient to compensate
for the decrease in the concentration of active BT-HAase and thus, the initial hydroly-
sis rate decreased. Then, when all the BT-HAase molecules had formed electrostatic
complexes with HA, the initial hydrolysis rate became equal to zero, which meant that
the concentration of active BT-HAase was nil. It should be noted that if BT-HAase in-
volved in electrostatic HA-BT-HAase complexes was catalytically active, no decrease
in the initial hydrolysis rate would have been observed at high HA concentrations
(Deschrevel et al., 2008a).
Figure 5.
Substrate-dependence of the HA hydrolysis catalyzed by BT-HAase in 5 mmol l
-1
ammonium acetate, at pH 5 and at 37°C, for a BT-HAase concentration of 2 g l
-1
. The number
average molar mass of HA was 1.45
×
10
6
g mol
-1
. The dashed line allows to distinguish between the
two characteristic parts of the atypical curve (see text). Data from Asteriou et al. (2006).


Search WWH ::

Custom Search