Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
isotherms) (Emmett, 1948). Gas separation may proceed in dynamic conditions when
a gas mixture is passing through a membrane or along the surface of a porous solid.
For the latter phenomenon, we have selected chromatographic tests.
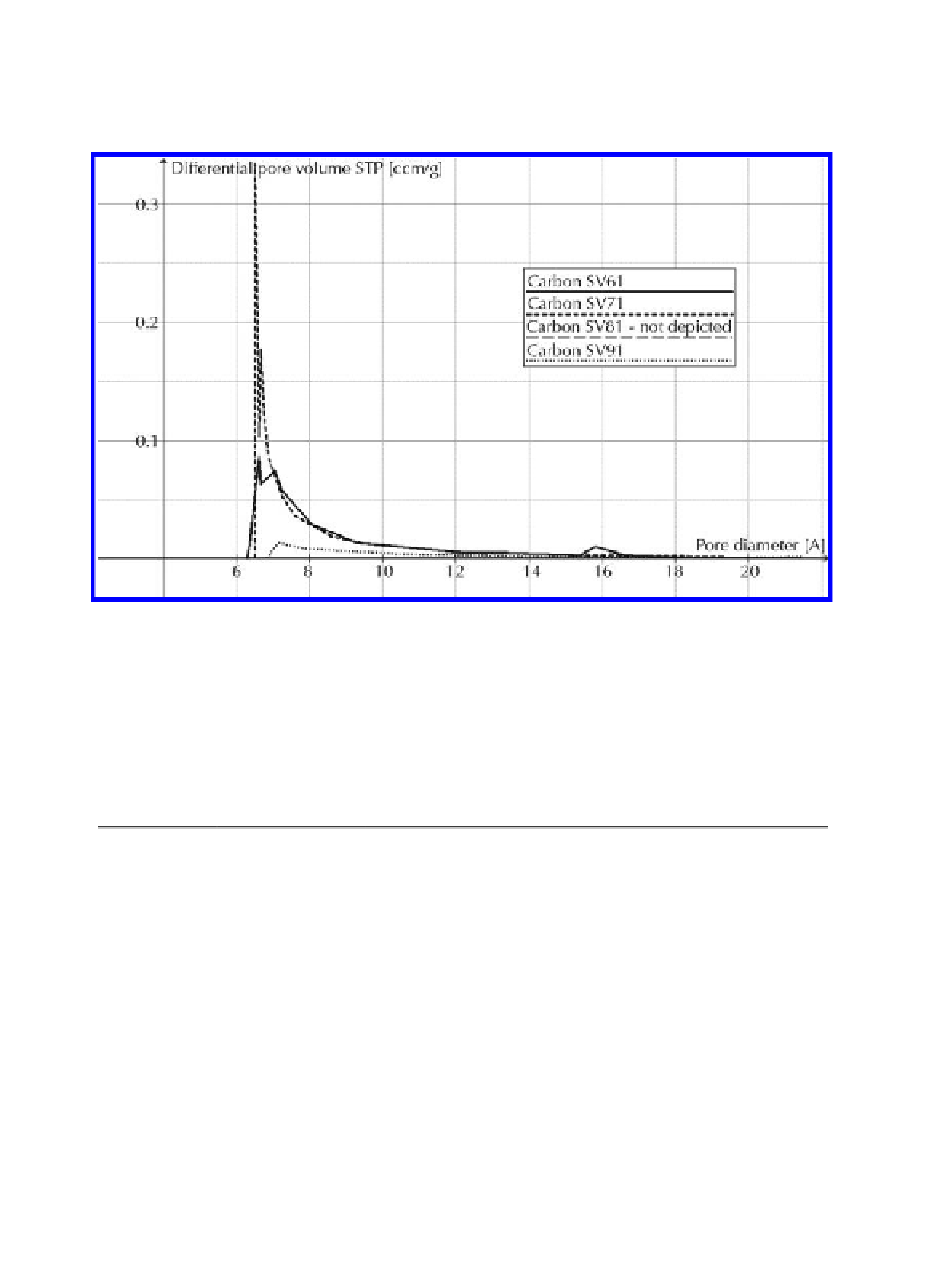
Figure 2.
Typical pore size distribution (PSD function) for carbon molecular sieves obtained by
pyrolysis of
Salix viminalis
wood. Symbols 6, 7, 8, 9 denote carbonization temperature of 600, 700,
800, 900°C, respectively. The PSD functions calculated basing from N
2
adsorption data at -196°C
and Hortvath-Kawazoe model.
table 1.
Atomic
and molecular dimensions of frequently used gas adsorbates.
Molecule
Kinetic diameter
[nm]
MIN-1
Smallest dimension of the
molecule [nm]
MIN-2
Intermediate dimension
perpendicular to MIN-1 [nm]
H
2
O
0.27
0.29
0.32
CO
2
0.33
0.32
0.33
Ar
0.34
0.35
0.36
Ne
0.28*
-
-
Kr
0.36*
-
-
O
2
0.35
0.29
0.30
N
2
0.36
0.30
0.31
CH
4
0.38
0.38
0.39
C
3
H
8
0.43
0.40
0.45
n-C
4
H
10
0.43
0.40
0.45
iso-C
4
H
10
0.50
0.46
0.60

Search WWH ::

Custom Search