Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Chapter 8
Bionanocomposites for multidimensional Brain Cell
signaling
Mark A. DeCoster, J. McNamara, K. Cotton, Dustin Green,
C. Jeyasankar, R. Idowu, K. Evans, Q. Xing, and Y. Lvov
iNtroduCtioN
Cell communication in the brain is dynamic, including electrical and chemical com-
ponents. These dynamics are utilized for maintenance of the highly complex commu-
nication pathways within and between cells of the brain, both in health and disease.
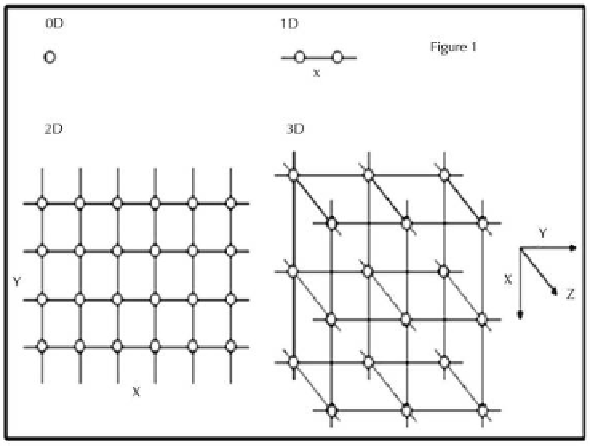
Bionanocomposites allow us to study brain cell function conceptually from 0 to 3
dimensions (03D), with 0D representing the single cell, 1D representing a linear ar-
rangement of two or more connected cells, 2D including cellular surface areas in both
X- and Y-dimensions, and 3D taking into consideration tissue scaffolds that include
X-, Y-, and Z-dimensions. These considerations are shown conceptually in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Visualization of cellular networks.
Using bionanocomposites, we are investigating how both normal brain cells and
brain tumor cells are communicating in multiple dimensions, identifying biocompat-
ible nanomaterials that can be used for experimental and modeling purposes.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search