Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 3.12. Examples of
anthropogenic effects on runoff.
(a) Runoff of the Inn at
Kajetansbrücke, Austria, illustrating
hydropower regulation effects on
runoff. Note the pattern of the
weekdays/weekend and 6 January as
a holiday (Epiphany). (b) Daily
runoff pattern at Vudee weir,
Tanzania, dominated by farmers
managing water diversions. During
the day farmers divert water
according to agreements with
downstream users. On Sunday they
release water for downstream use.
On Wednesday a nearby group of
farmers are allowed to irrigate.
From Mul et al.(
2011
).
100
a)
80
60
40
20
0
Jan 1
Jan 15
Jan 22
Jan 29
Jan 8
25
Sun
Mon
Tue
Wed
Thu
Fri
Sat
20
15
10
5
b)
0
Sep 9
Sep 10
Sep 11
Sep 12
Sep 13
Sep 14
Sep 15
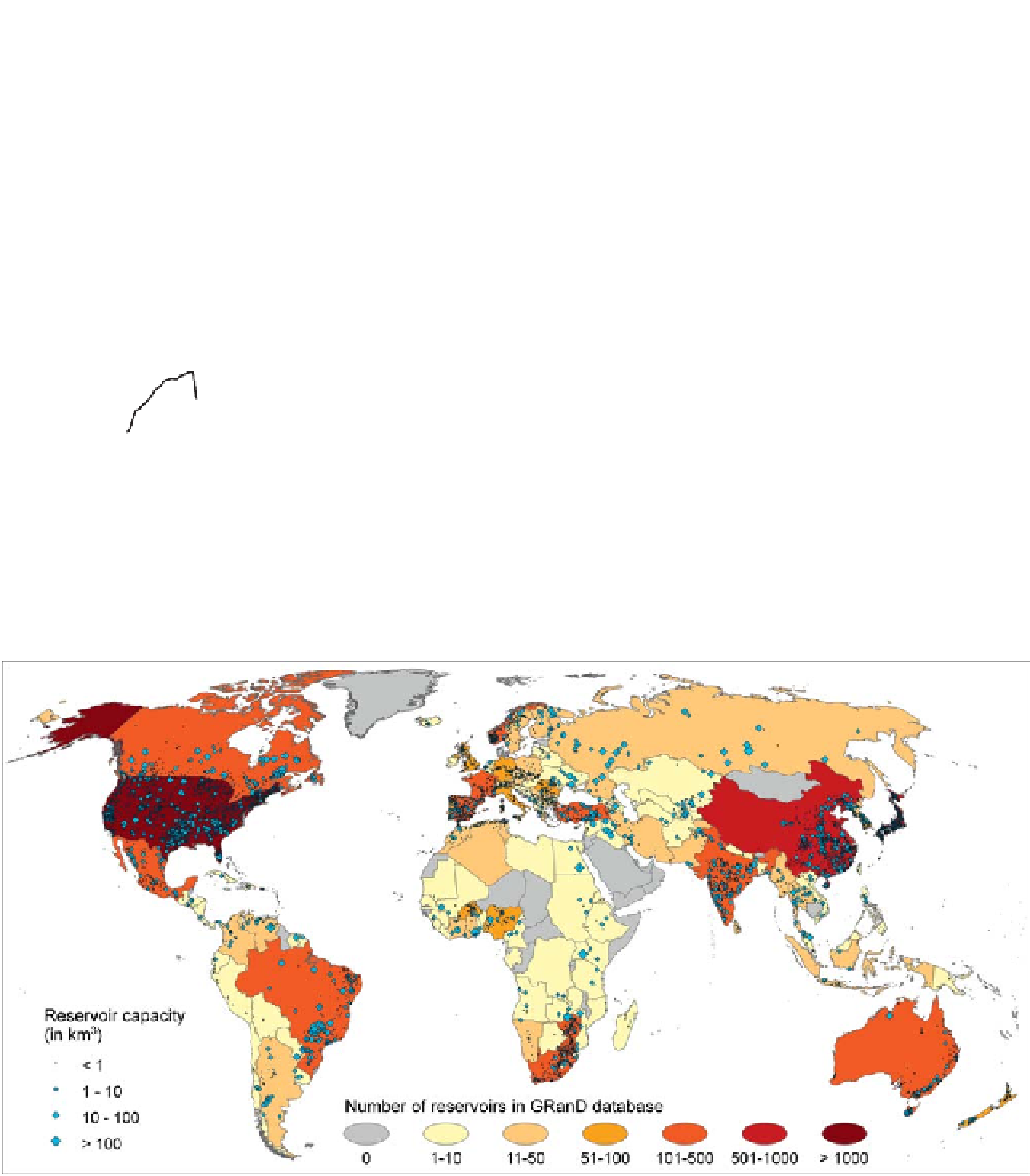
Figure 3.13. Global distribution (by country) of large reservoirs. From Lehner et al.(
2011
).
Snowmelt-dominated water inputs and warm, sunny,
dry summers in the region lead to strong seasonality of
hydrological behaviour, starting with a long winter period
of frozen ground and snow accumulation that can last from
November until June. During this period, runoff is minimal
and the catchment stores water in the snowpack for more
intense melt delivery with spring snowmelt. The duration
and intensity of annual snowmelt is climate dependent and


































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search