Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
uncertainty to be expected, including data, model and
parameter uncertainties. This method of uncertainty esti-
mation is complementary to other methods such as Monte
Carlo simulations.
Comparative assessment of the performance of runoff
predictions amongst a range of methods, and in many
ungauged basins around the world, will give generalised
estimates of the predictive uncertainty and a generalised
understanding of the factors controlling it. In this way it
will shed light on the co-evolution of catchments. It will
provide guidance on what methods to choose in particu-
lar environments and why, and will thus provide a
benchmark to guide any future progress on predictions
of runoff in ungauged basins.
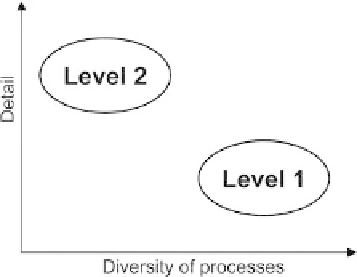
Figure 2.12. Definition of Level 1 and Level 2 assessments. Detail
relates to the amount of information available on predicting runoff
signatures in a particular catchment, such as the predictive errors and
catchment/climate characteristics. Diversity of processes relates to
the spectrum of hydrological processes covered in the comparative
assessment, from a small diversity if only a few regions are examined
to a large diversity if many regions worldwide are examined.
A comparative assessment (blind testing) of the predic-
tions of runoff signatures (annual runoff, seasonal run-
off, flow duration curve, low flows, floods and runoff
hydrographs) in ungauged basins is performed in this
topic, as part of a synthesis across processes, places and
scales, at two different levels. The Level 1 assessment is
a meta-analysis from the extensive published literature.
The Level 2 assessment is a more detailed analysis of
numerous individual catchments from around the
world, selected from the studies reported in the litera-
ture. In each case, predictive performance is analysed in
a comparative way as a function of climate and catch-
ment characteristics,
Understanding hydrological similarity is the basis for
our ability to predict runoff in ungauged basins, extrapo-
lating from gauged to ungauged basins within a homo-
geneous region, based on either statistical or process-
based methods.
Runoff predictions in ungauged basins are associated with
considerable uncertainty. Assessing the performance of
the predictions will give an estimate of
the prediction method and data
the total
availability.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search