Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
performance (blind testing) of the predictions of various
runoff signatures, has formed the basis for comparison of
predictive techniques in thousands of catchments from
around the world.
Over the past decade, the IAHS PUB initiative has been
the catalyst for a range of research activities organised
around six PUB themes, and executed through a large
number of national, regional and global PUB working
groups. These themes, in abbreviated form, are: (i) catch-
ment similarity and classification, (ii) conceptualisation of
process heterogeneity, (iii) uncertainty analysis and model
diagnostics, (iv) new data collection approaches, (v) new
hydrological theory and (vi) new modelling approaches.
These are also reflected in the frontispiece to this topic, and
also figure prominently in the guide to PUB best practice
that appears in
Chapter 13
(Recommendations). These
research activities have contributed substantially to the
literature, and have led to significant advances to the
various elements of PUB.
This topic firmly builds on the progress achieved during
the PUB decade. Separate chapters have been devoted to
(i) data collection approaches and learning from the data,
and (ii) exploration of flow paths and storage as a way to
understand the role of heterogeneity. Hydrological similar-
ity is a recurring theme in every chapter, and is the basis for
regionalisation approaches. The topic has included a plur-
ality of models and modelling approaches for predictions
of the various runoff signatures, and has discussed their
relative strengths and weaknesses. Uncertainty assessment
through cross-validation in thousands of catchments from
around the world has been another recurrent theme.
Finally, the synthesis across processes, places and scales
has given rise to a higher level synthesis of different
theoretical
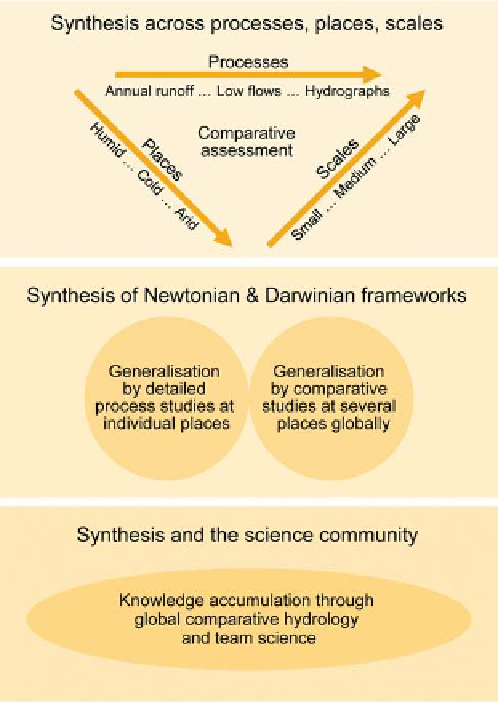
Figure 12.1. Organisation of the chapter: (top) synthesis through
comparative assessment, (middle) approaches to generalisation
through a higher level synthesis, and (bottom) knowledge
accumulation through global comparative hydrology.
frameworks of how to approach the PUB
highlighting successes, areas of persistent confusion, and
opportunities for further research.
This chapter is organised into three parts (
Figure
12.1
). The first part presents the outcomes of the syn-
thesis across processes, places and scales carried out in
the form of comparative performance assessment of
methods used for predicting the various runoff signa-
tures, and the inferences that could be drawn from this
assessment for advancing predictions. The second part
of the chapter extends this discussion to include
approaches needed to develop generalised understand-
ing, through a higher level synthesis of Newtonian
(detailed process studies in individual places) and
Darwinian (comparative studies at several places glob-
ally) approaches. Finally, the third part of the chapter
discusses the implications for the PUB community to
facilitate knowledge accumulation through improved
organisation and communication.
problem.
The specific outcomes of the comparative assessment
reported in this topic reflect the lessons learned from the
diversity offered by nature
s own experiments, covering
about 25 000 catchments, and as expressed through thou-
sands of observational, modelling and prediction studies
surveyed. The outcomes of these studies are presented in
hundreds of published articles that we reviewed; many of
them were carried out within the last decade and were
inspired by PUB. Most of the 130 contributors to this topic
are themselves members of the PUB community, and
served as experts to summarise the state of the art of
hydrological knowledge and predictions of the various
runoff signatures. In these ways, the outcomes of the topic
represent the collective wisdom of the broad hydrology
community, including the PUB community. The remainder
of this chapter summarises the outcomes of the findings
of
'
the synthesis across processes, places and scales,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search