Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
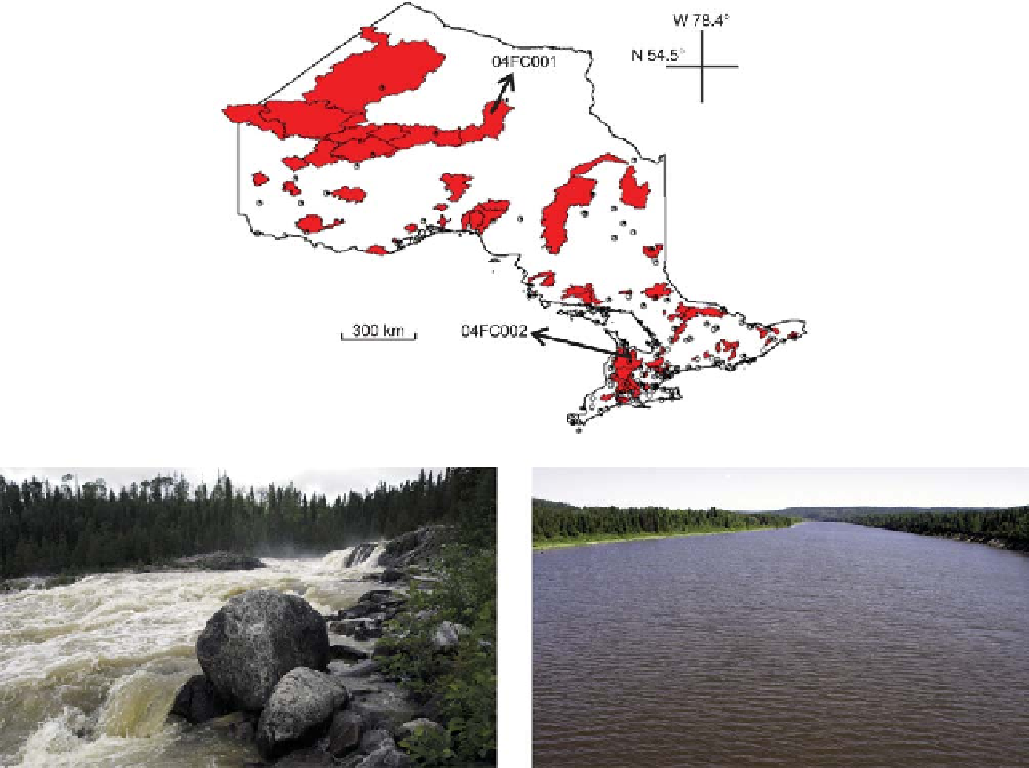
Figure 11.28. Locations of rainfall (white circles) and temperature (black dots) stations and gauged basins (red). Labels indicate the names of the
basins selected for illustrating the model application results. (Left) location 04FC001, (right) location 04FC002. Adapted from Samuel et al.
(
2011b
).
(
1976
). The MAC-HBV model structure takes advantage
of some of the salient features of the model developed by
Seibert (
1999
) and the one proposed by Merz and Blöschl
(
2004
). The model uses Brent
(iii) changing the objective function in the optimisation
procedure by including additional criteria for model
assessment on low flows. A summary of the changes
implemented in each variant of the MAC-HBV model is
presented in
Table 11.5
, while the details can be found in
Samuel et al.(
2011b
).
The best MAC-HBV model variant identified was then
combined with the dual regionalisation method (IDW-PS)
for continuous flow estimation in ungauged basins. The
dual or combined regionalisation approach (IDW-PS)
takes advantage of both spatial proximity and physical
similarity methods. In this approach, the basins are first
grouped based on their physical similarity using a cosine-
similarity method, and subsequently model parameters are
transferred using the IDW approach for only the similarly
grouped sites. In a comprehensive inter-comparison study,
it was shown that
s parabolic interpolation
(Press et al.,
1992
) to generate the optimised model par-
ameter set.
To identify the optimal rainfall
'
runoff model structure
that can improve both the estimation of baseflow and
average daily runoff, five variants of the original MAC-
HBV model (Model 0) have been investigated and tested
in 111 basins. The variation in the MAC-HBV models
includes: (i) extending possible ranges of maximum and
minimum model parameters, especially related to deep
soil and slow flow model parameters; (ii) modifying the
model structure, e.g., by applying a non-linear storage
discharge relationship, instead of a linear one, in the deep
soil
-
layers (in the hillslope routing components); or
the IDW-PS approach is the best
Search WWH ::

Custom Search