Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 9.13. Parameters of the GEV
distribution as a function of drainage
area fitted to annual maximum peak
runoff in the eastern USA. From
Villarini and Smith (
2010
).
10000
1000
100
10
1
1000
100
10
1
0.8
0.4
0.0
-0.4
100
1000
10000
100000
Drainage area (km
2
)
together is also behind the index flood method (Dalrymple,
1960
; Hosking and Wallis,
1997
). The method involves the
formation of a collection of catchments, not necessarily
geographically contiguous, that can be considered to be
similar in terms of hydrological response, as discussed in
Section 9.2.3
. The index flood method estimates the T-year
flood as the product of a scale factor, which is called the
index flood (often defined as the mean or median annual
maximum flood), and a growth factor, which describes the
relationship between the dimensionless flood and the
return period, T (the so-called growth curve). In general
etc. In the simplest case, a regression can be used to
approximate f (see
Section 9.3.1
), but more complex
methods exist such as geostatistics or process-based
methods (see e.g., Bocchiola et al.,
2003
and the following
sections). Hereafter the focus is on the estimation of the
growth curve g(T).
Farquharson et al.(
1992
) observed that climate seems to
be the principal factor in determining the shape of regional
flood frequency curves (i.e., of the growth curves).
Figure
9.14
shows flood growth curves estimated using annual
maximum flood series from catchments in different semi-
arid and arid regions from 12 countries in five continents.
As discussed in
Section 9.2
, climate is one of the controls
on the shape of the flood frequency curve, which is very
evident in
Figure 9.14
where the growth curves in arid
catchments have much higher slope (i.e., variability) and
skewness (i.e.,
q
T
¼
g
ð
T
Þ
f
ð
A, P, S,
:::Þ
ð
9
:
2
Þ
where g(T) is called the growth curve and the index
flood is expressed as a function of climatic and catchment
characteristics such as area, mean annual precipitation
'
propensity to outliers
'
) than in humid




































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































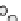




















































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search