Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
400
500
Ql = 0.69
Ql=0.88
400
300
300
200
200
100
100
0
0
J
FM A
M
J
J
A
SO
N
D
J
FM A
M
J
J
A
SO
N
D
Positive budget
Negative budget
Positive to negative budget
600
Ql = 0.13
Ql=0.25
300
500
400
200
300
200
100
100
40 km
0
0
J
J
J
J
J
J
FM A
M
A
SO
N
D
FM A
M
A
SO
N
D
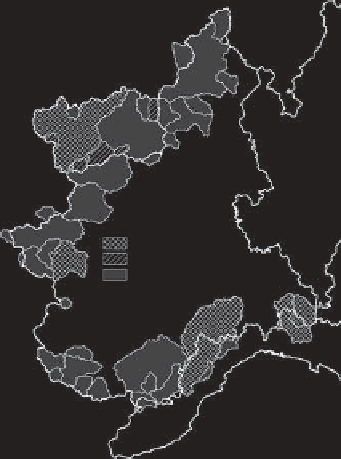
Figure 6.20. Modelled vs. observed monthly runoff curves in north-western Italy. (a) Study domain and the catchments used for the model
application; (b) observed (solid line) and simulated (dashed line) flow regime curves, along with confidence bands of observed runoff at 40%
(80%) for four representative catchments: Savara at Eau Rousse, Sesia at Ponte Aranco, Rutor at Promise, and Toce at Candoglia. In the
upper right corner of each panel a measure of model performance, the quality index, QI, is reported. From Bartolini et al.(
2011
).
highlight the strong seasonality of the high mountain
catchments of the region due to snow processes.
A downscaling method was proposed by Schreider et al.
(
2002
). They first calibrated a rainfall
predicted with modest accuracy: the mean absolute error
was 25.4% of the gauged value, and 52% of the streams
had errors less than 20%. The authors suggested that the
main causes for the prediction errors were the gridded
climate data, especially precipitation for areas with sparse
gauges. In any case, the model was clearly able to distin-
guish various regime types, i.e., between pluvial, hybrid
and melt-dominated.
A typical example of a rainfall runoff model where the
simulations are performed at a daily time step and runoff
is then aggregated to a monthly time step has been pre-
sented by Zappa (
2002
) and Viviroli and Weingartner
(
2012
). They simulated runoff for all of Switzerland
(41 000 km
2
) using the PREVAH model (Viviroli et al.,
2009a
), using daily meteorological data at a resolution of
500 × 500 m
2
as an input. They first used a-priori model
parameters (termed
runoff model to data
at the outlet of a catchment, and then predicted mean
monthly runoff at each grid cell within this catchment
applying a downscaling technique based on a topographic
index similar to the wetness index (Beven et al.,
1995
).
They tested the model for two catchments in northern
Thailand and obtained an accuracy of 13
-
17% of the
relative error at the monthly time step. Yet another param-
eter regionalisation method based on kriging was proposed
by Vandewiele and Elias (
1995
) and tested on catchments
in Belgium. Moore et al.(
2012
) assessed the accuracy of a
simple grid-based monthly water balance model in British
Columbia in western Canada. Monthly mean runoff was
estimated at all grid cells, which were then aggregated to
estimate the corresponding runoff values for a number of
gauged catchments in the region. The model was imple-
mented without calibration, using a-priori parameter
values that are based on either previous studies or the
authors
-
in
Figure 6.22
). In a
second step they adjusted the model parameter based on
water balance data from about 200 gauged catchments
(Schädler and Weingartner,
2002
). The resulting simula-
tions are from the optimised model. Model verifications
by Pfaundler and Zappa (
2009
) included comparisons
against measured monthly runoff (
Figure 6.22
).
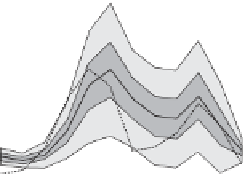
Figure 6.23
shows local mean monthly runoff in August
simulated by this model in a perspective view. It high-
lights the large gradient from the pre-alpine zone near
Lake Thun to the high mountains where the catchments
are ice fed. From a hydrological point of view, this
visualisation is misleading since it suggests a spatially
'
initial model
'
past experience. The results are presented in
Figure 6.21
, in which the left-hand column presents some
of the more successful results, while the right-hand column
presents some of the less successfully reproduced hydro-
graphs. The water balance model was demonstrated to be
robust at predicting the relative magnitudes of monthly
runoff in terms of rank, but is not consistently effective at
predicting the Pardé coefficients. Also, annual runoff is
'




























































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search