Database Reference
In-Depth Information
If a
fuzzy cardinality constraint
exists then the DBMS must compute the number of
subclasses to which each superclass instance belongs to; for example, in order to decide
if the number of subclasses of a superclass instance is between “approximately_2”
and “approximately_half” of existing subclasses. However, this number is not simple,
because membership is now fuzzy. This problem may be solved in two ways: a) By
using the fuzzy set cardinality (Pedrycz et al., 1998) of the second point of view fuzzy
set or by using generalized measures, like the fuzzy set energy (De Luca et al., 1974),
b) By counting the number of subclasses with a membership degree greater than a
minimum value (usually zero). Once the DBMS has computed this number, the system
must check if this number satisfi es the fuzzy cardinality constraint.
2.
FUZZY ATTRIBUTE DEFINED
SPECIALIZATIONS
There are some kinds of fuzzy attributes, summarized in (Galindo et al., 2001a). Some
models (Medina et al., 1994) and applications (Galindo et al., 1998; Galindo, 1999) use the
following ones. The so-called fuzzy attributes Type 1 are totally crisp (traditional), but they
have some linguistic trapezoidal labels defi ned on them, which allow us to make the query
conditions for these attributes more fl exible (cold, warm...). With these attributes we can use
fuzzy queries in classic databases. Fuzzy attributes Type 2 admit crisp or fuzzy data over
an ordered underlying domain. Fuzzy attributes Type 3 do not have an ordered underlying
domain, for instance the hair color. On these attributes some labels are defi ned (fair, brown,
red-haired...) and on these labels a similarity relation has yet to be defi ned. Thus, each two
labels are equal (or similar) with a similarity degree in [0,1]. Besides fuzzy attributes, Type
3 admits fuzzy sets (or possibility distributions) on its underlying domain. An example of
these fuzzy sets is {1/brown, 0.5/red haired, 0.2/fair}. In some contexts a fuzzy attribute
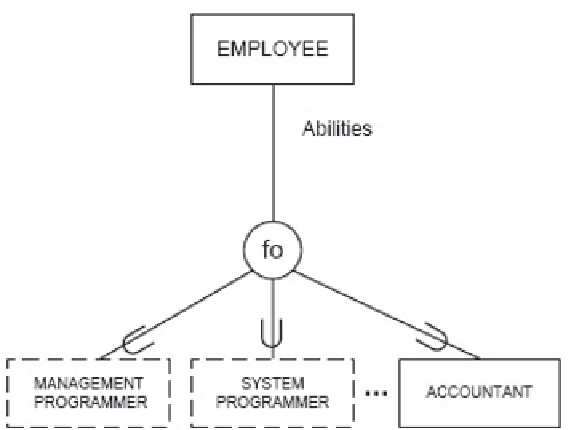
Figure 8: Example 7. Fuzzy overlapping specialization