Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
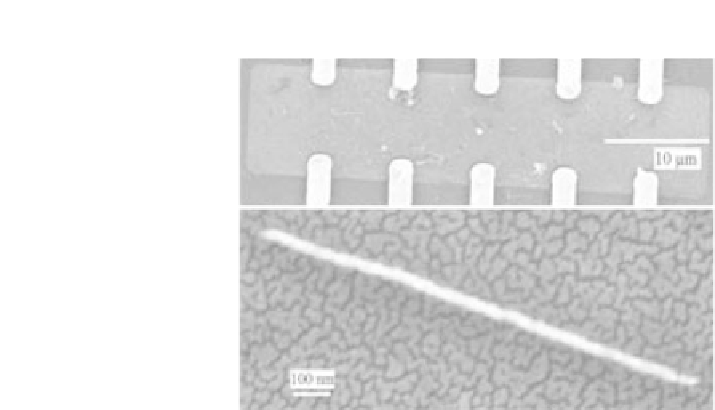
Figure
11.8.
An assembled nanocell that exhibited memory with 10 pins (top);
one of the metallic nanowires interspersed with electroactive molecules as the
active elements (bottom) [79].
We have synthesized several types of room temperature-operable molecular
switches and demonstrated them in nanopores and atop silicon-chip platforms.
The functional molecular switches can be reversibly switched from an ''off '' state
to an ''on'' state, and/or the reverse, based on stimuli such as voltage pulses. The
number of nanoparticles (usually metallic or semiconducting) and the number of
the interconnecting molecular switches can vary dramatically based on the chosen
size of the nanocell and on the dimensions of the nanoparticles and molecules
chosen.
Within the fabricated nanocell, the input and output leads could be repeti-
tively interchanged based on the programming needs of the system, thereby
demonstrating the pliability of the architecture. Naturally, issues of gain will
eventually have to be addressed through either an underlying CMOS layer or
clocked circuits programmed into the nanocell [82]. Even if one CMOS transistor
was used for gain at the output from each nanocell, enormous space savings could
be attained since a nanocell could possess the functionality of numerous
transistors working in concert to produce a specified logic function. Furthermore,
by capitalizing on the NDR properties of the molecular switches, internal gain
elements based upon NDR/nanoparticle/NDR stacks (Goto pairs [83]) could be
efficacious.
The object in programming or training a nanocell is to take a random, fixed
nanocell and turn its switches ''on'' and ''off'' until it functions as a target logic
device. The nanocell is then trained post-fabrication by changing the states, ''on''
or ''off,'' of the molecular switches by imposing voltages at the surrounding input/
output leads. Notice how we hope to address, in a broad sense, the internal
molecular switches via the surrounding leads.





Search WWH ::

Custom Search