Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
A
L
B
K
C
J
D
I
E
H
F
G
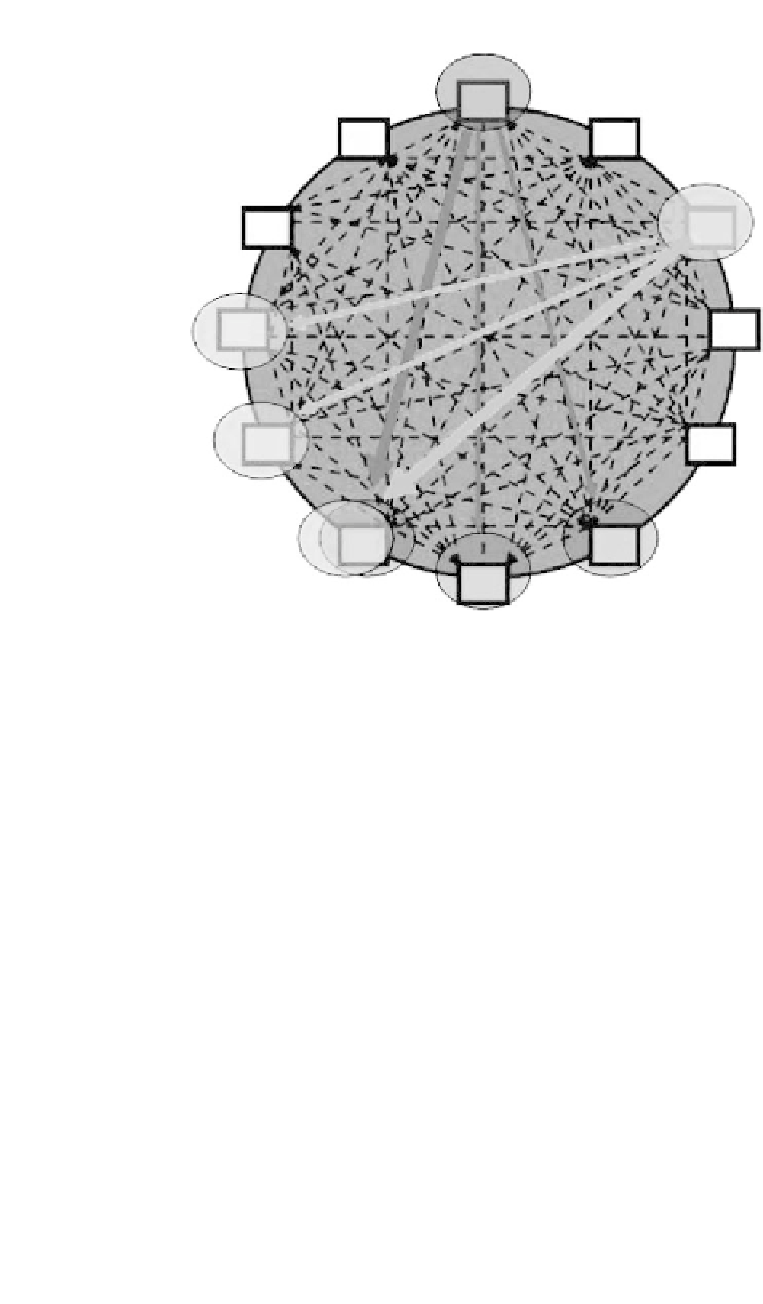
Figure
8.12.
Multiple broadcasting on disjoint sets of receivers.
architectures. This feature allows multiple braodcasting to sets which are not disjoint.
This is basically the combination of concurrent receive and multiple broadcasting.
Assume the scenario shown in the Figure 8.12 where one of the A's and C's
destinations is the same (node H). This requires the sending frequency of A and C
to be the same as the receiving frequency of H. However, if the sending frequency
of these two nodes are the same, the receiving frequency of K, J, G,andF has to be
the same too, which causes each of these nodes to receive the superposition of the
signals sent by A and C.
One approach to solve this problem, is using phased array techniques
explained in [32] to direct the waves to specific locations. It is also possible to
combine the phased array technique with multiple frequencies. As a result, for
each frequency, some of the waves are only transmitted to desirable directions and
are received by the intended sources.
8.4. CONCLUSIONS
In this chapter, the algorithm design aspects of the spin-wave reconfigurable mesh,
spin-wave crossbars, and spin-wave fully interconnected were studied. The
architectures simultaneously transmit multiple signals using different frequencies,




Search WWH ::

Custom Search