Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
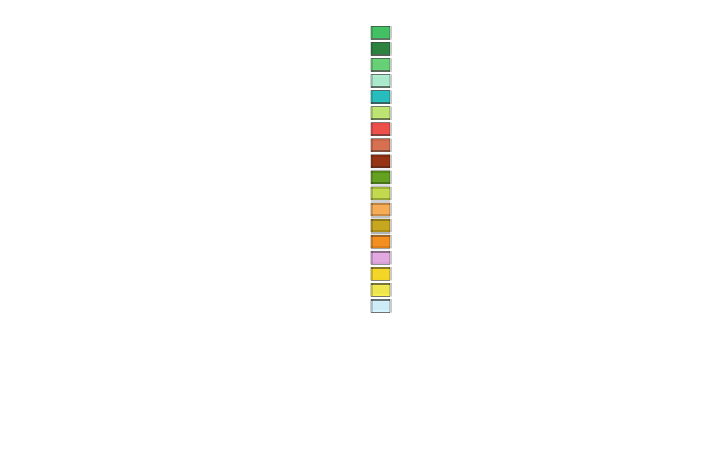
Boreal/montane forest
70
PLASIM + CARAIB
6600-6500 BP
Cool temperate mixed forest
Cool temperate conifer forest
Temperate broadleaved deciduous forest
Warm temperate mixed forest
Warm temperate conifer forest
Warm temperate broadleaved evergreen forest
Sub-tropical forest
Tropical seasonal forest
Tropical rainforest
Cold temperate/boreal open woodland
Warm temperate open woodland
Tropical savanna
Temperate grassland
65
60
55
50
45
Tropical grassland
40
Tundra
Semi-desert
Desert
Ice or polar desert
35
30
-10 -5
0
5 10 15
20 25 30 35 40
Longitude(
°
)
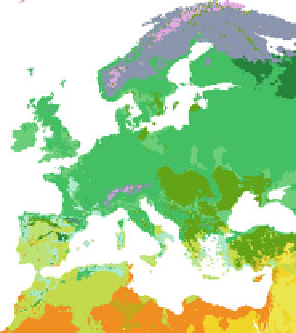
Fig. 1 European vegetation distribution for 6 ka BP, simulated by the high-resolution vegetation
model CARAIB forced with PLASIM climate
Fig. 2 Fraction of agricultural activity versus foraging subsistence at a critical transition time
(6,900 years BP/4950 BC), when the GLUES-simulated frontier between farmers and foragers ran
across central Europe
range of anthropogenic activities, and the Early Anthropocene hypothesis (Kaplan
et al.
2011
; Lemmen
2010
).
Simulations of the transition to agriculture (Fig.
2
) agree with archeological site
data across Western Eurasia within a model uncertainty of
500 years (Lemmen
and Wirtz
2012
; Lemmen et al.
2011
). Thus, GLUES is able to realistically simulate
the onset of agriculture not only on a global scale as previously reported (Wirtz and
±


















































































































































































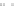


































































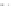


















































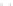




























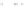




































































































































































































































































































































































































































































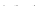








































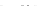
















































































































































































































































































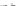






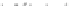



































































































































































































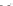

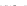


































Search WWH ::

Custom Search