Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
28 000
12 000
20 000
10 000
8000
12 000
6000
Magnetic
4000
4000
Radiometric
2000
0
50 m
20
Argillites
and
quartzites
40
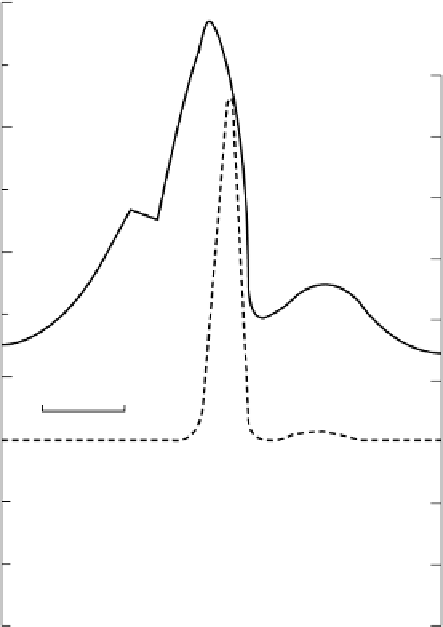
Fig. 10.3
Radiometric and magnetic
profiles over pitchblende-magnetite
mineralization in Labrador. (After
Telford
et al
. 1990.)
Mineralized
zones
Boreholes
60
monitored then provides a diagnostic means of discrimi-
nating between different sources. Figure 10.2 shows the
gamma ray spectra of
238
U,
232
Th and
40
K and it is ap-
parent that measurements at 1.76, 2.62 and 1.46 MeV,
respectively, provide a discrimination of the source
(1 MeV = 10
6
electronvolts, 1 electronvolt being the
energy acquired by a particle of unit charge falling
through a potential of 1 volt). These devices are some-
times termed
pulse-height analysers
as the intensity of
the scintillation pulses is approximately proportional to
the original gamma ray energy.
Gamma ray spectrometers for airborne use are often
calibrated by flying over an area of known radioisotope
concentration or by positioning the aircraft on a concrete
slab fabricated with a known proportion of radio-
isotopes. The actual concentrations of
238
U,
232
Th and
40
K in the field can then be estimated from survey data.
noble gas it does not form compounds with other ele-
ments and moves freely through pores, joints and faults
in the subsurface either as a gas or dissolved in ground-
water. It is one of the products of the
238
U decay series,
with a half-life of 3.8 days, and the presence of
222
Rn at
the surface is often an indication of buried uranium
concentrations.
The
radon emanometer
samples air drawn from a
shallow drillhole. The sample is filtered, dried and
passed to an ionization chamber where alpha particle
activity is immediately monitored to provide a count
rate.
The emanometer is relatively slow to use in the field.
It does, however, represent a means of detecting deeper
deposits of uranium than the other methods described
above, since spectrometers will only register gamma
rays originating in the top metre or so of the subsurface
(Telford 1982). Because of its high mobility, radon can
have travelled a considerable distance from the source of
uranium before being detected. The emanometer has
also been used to map faults, which provide channels for
10.4.4 Radon emanometer
Radon is the only gaseous radioactive element. Being a