Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
Linear Regression
6
Regression line
Regression line:
y = b
0
+ b
1
x
5
∆
y
4
∆
x
3
∆
y=b
1
i-th data point ( x
i
,y
i
)
2
∆
x=1
1
0
0
1
2
4
5
6
8
3
7
x
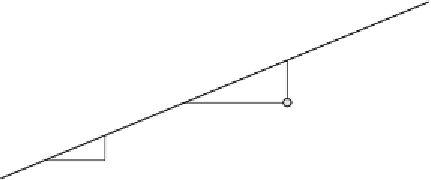
Fig. 4.4
Linear regression. Whereas classical regression minimizes the ¨
y
deviations, reduced
major axis regression minimizes the triangular area 0.5*(¨
x
¨
y
) between the points and the
regression line, where ¨
x
and ¨
y
are the distances between the predicted and the true
x
and
y
values. The intercept of the line with the
y
-axis is
b
0
, whereas the slope is
b
1
. These two
parameters defi ne the equation of the regression line.
errors as its magnitude cannot be determined accurately. Linear regression
minimizes the ¨
y
deviations between the
xy
data points and the value pre-
dicted by the best-fi t line using a least-squares criterion. The basis equation
for a general linear model is
where
b
0
and
b
1
are the coeffi cients. The value of
b
0
is the intercept with the
y
-axis and
b
1
is the slope of the line. The squared sum of the ¨
y
deviations
to be minimized is
Partial differentiation of the right-hand term and equation to zero yields a
simple equation for the fi rst regression coeffi cient
b
1
: