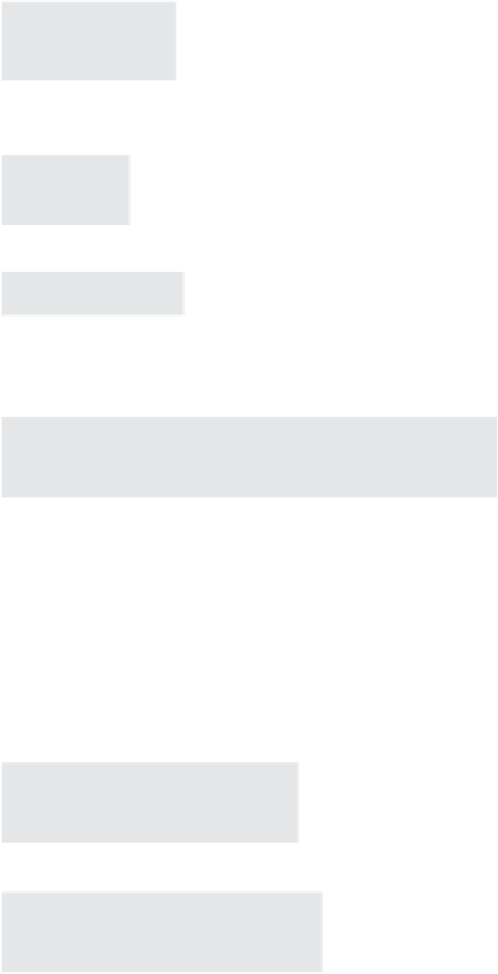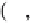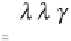Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
kriging uses a weighted average of the neighboring points to estimate the
value of an unobserved point:
where
are the weights which have to be estimated. The sum of the weights
should be one to guarantee that the estimates are unbiased:
λ
ι
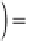
The expected (average) error of the estimation has to be zero. That is:
where
z
x
0
is the true, but unknown value. After some algebra, using the pre-
ceding equations, we can compute the mean-squared error in terms of the
variogram:
where
E
is the estimation or
kriging variance
, which has to be minimized,
γ(
x
i,
x
0
) is the variogram (semivariance) between the data point and the un-
observed,
γ(
x
i,
x
j
) is the variogram between the data points
x
i
and
x
j
, and
λ
i
and
λ
j
are the weights of the
i
th and
j
th data point.
For kriging we have to minimize this equation (quadratic objective func-
tion) satisfying the condition that the sum of weights should be one (linear
constraint). This optimization problem can be solved using a Lagrange mul-
tiplier
resulting in the
linear kriging system
of
N
+1 equations and
N
+1
unknowns:
ν
After obtaining the weights
λ
i
, the kriging variance is given by
The kriging system can be presented in a matrix notation: