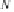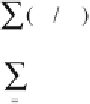Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
Grid Point
Control Point
a
b
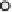
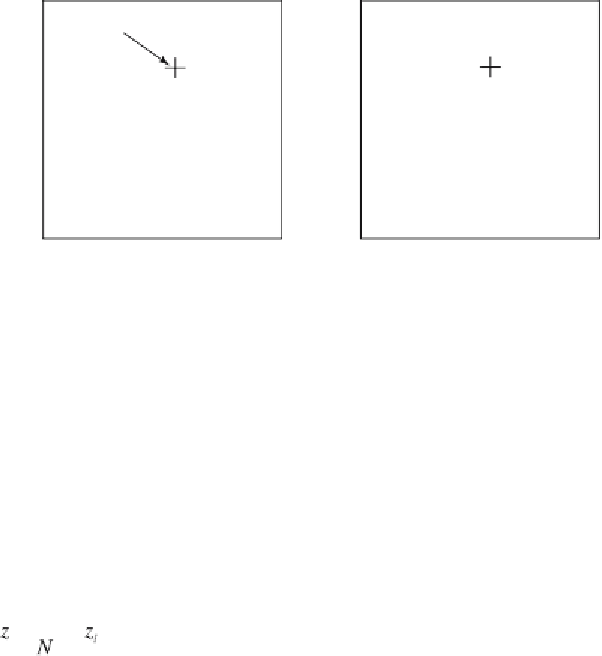
Fig. 7.5
Methods to select the control points for estimating the grid points.
a
Construction of
a circle around the grid point (plus sign) with a radius defi ned by the spatial autocorrelation
of the
z
-values at the control points (circles).
b
Triangulation. The control points are selected
from the apices of the triangles surrounding the grid point and optional also the apices of the
adjoining triangles.
The second step of surface estimation is the actual computation of the
z
values of the grid points. The
arithmetic mean
of the
z
values at the control
points.
provides the easiest way of computing the grid points. This is a particularly
useful method if there are only a limited number of control points. If the
study area is well covered by control points and the distance between these
points is highly variable, the
z
values of the grid points should be computed
by a
weighted mean
. The
z
values at the control points are weighted by the
inverse distance
d
i
from the grid points.
Depending on the spatial scaling relationship of the parameter
z
, the inverse