Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1000
800
.
600
For strain rates
ε
from 5.3 x 10
−
5
to 3.3 x 10
−
3
%/s
400
200
0
0
8
16
24
Axial strain (
ε
y
), %
(a)
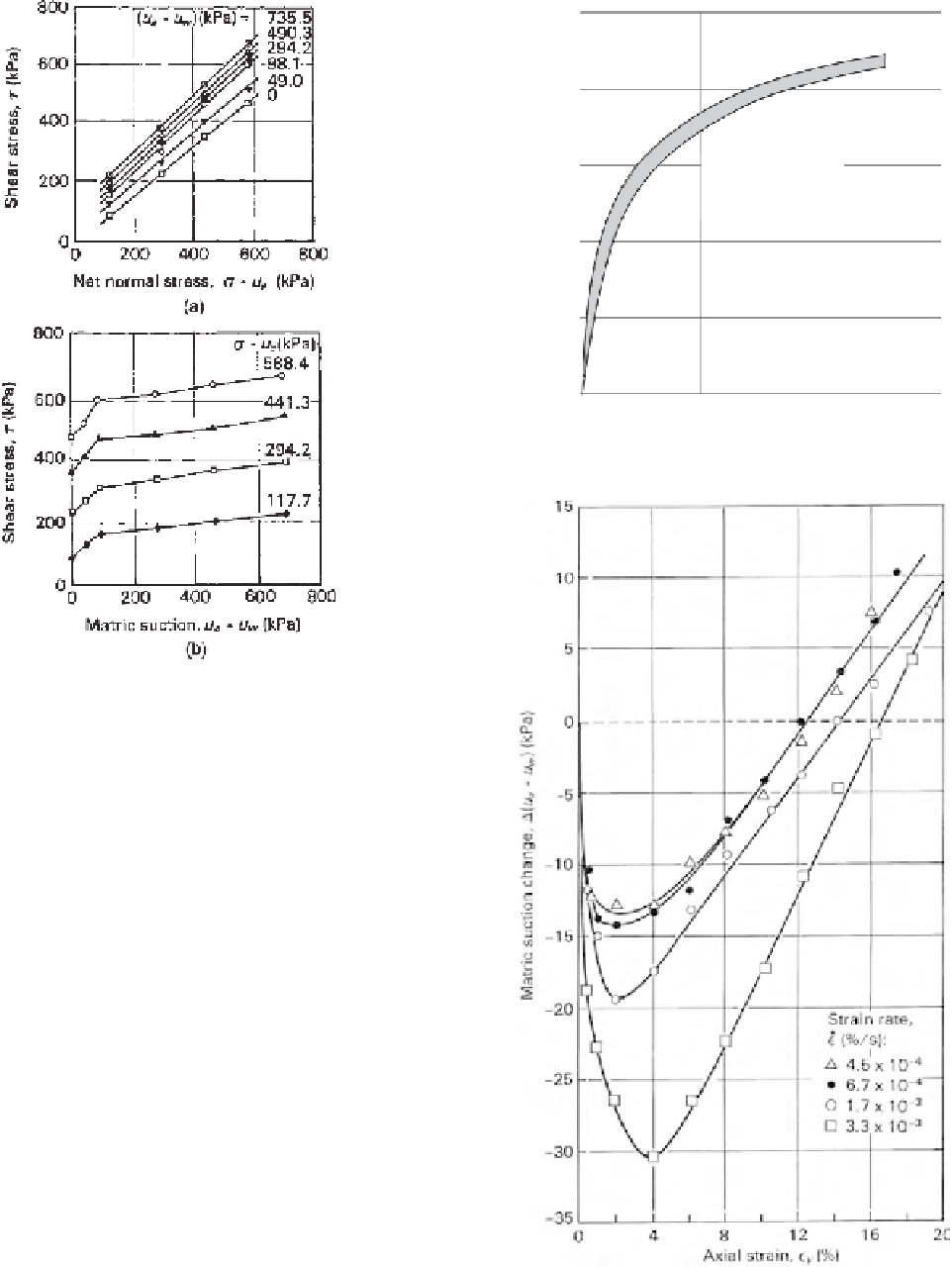
Figure 11.82
Direct shear tests on compacted Madrid clayey
sand: (a) horizontal projection of failure envelope onto shear
strength versus
σ
u
a
plane; (b) horizontal projection of failure
envelope onto shear strength versus
u
a
−
−
u
w
plane (after Escario
and Saez, 1986).
11.9.2 Strain Rates for Triaxial Tests
Strain rate can be defined as the rate at which a soil specimen
is axially compressed:
ε
f
t
f
ε
˙
=
(11.32)
where:
˙
ε
=
strain rate for shearing a specimen in the triaxial
test,
ε
f
=
strain of the soil specimen at failure, and
t
f
=
time required to fail the soil specimen, or “time to
failure.”
The strain at failure,
ε
f
, depends on the soil type and the
stress history of the soil. Table 11.8 presents typical val-
ues of strain at failure,
ε
f
, obtained from numerous triaxial
testing programs on unsaturated soils. The information in
Table 11.8 can be used as a guide when determing a suitable
strain rate
(b)
Figure 11.83
Effect of strain rate for constant-water-content
tests on Dhanauri clay: (a) effect of strain rate on deviator stress;
(b) effect of strain rate on matric suction change (after Satija, 1978).
ε
for shear strength testing.
˙






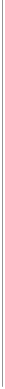





Search WWH ::

Custom Search