Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
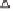
deviate from the effective angle of internal friction (i.e., 32
◦
)
as the air-entry value of the soil was exceeded (Fig. 11.72).
considerable dilation and postpeak strain softening. The vol-
umetric strain remained essentially constant when the devi-
ator stress was constant.
Figure 11.72 shows the projection of shear stresses at fail-
ure,
τ
f
, onto the
τ
versus
u
a
−
11.8.4 Undrained and Unconfined Compression Tests
Six series of undrained and unconfined compression tests
(i.e., UC) on unsaturated compacted specimens were per-
formed by Chantawarangul (1983). The soil was clayey sand
consisting of 52% sand, 18% silt, and 30% clay. The soil had
a liquid limit of 30%, a plastic limit of 19%, and a shrink-
age limit of 16%. The soil was compacted using a miniature
Harvard apparatus to give high- and low-density specimens
at various water contents. The water contents were generally
on the dry side of optimum. The high- and low-density spec-
imens correspond to dry density values of approximately
1800 and 1700 kg/m
3
, respectively.
u
w
plane for the CW tests.
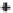
The effective angle of internal friction,
φ
, of the compacted
kaolin was found to be 32
◦
.The
φ
b
angle was found to be
the same as the effective angle of internal friction,
φ
(i.e.,
32
◦
), at low matric suction values. The
φ
b
angle decreased
to as low as 12
◦
at high matric suctions. The matric suction
at the inflection point of the relationship between
φ
b
and
matric suction increased with an increase in the net confin-
ing stress, as shown in Fig. 11.73. In other words, the net
confining stress had an effect on the nonlinearity of the
φ
b
angle for the CW tests on compacted kaolin specimens. The
shear strength versus matric suction relationship started to
700
σ
3
σ
σ
σ
σ
σ
3
-
u
a
-
u
a
-
u
a
-
u
a
-
u
a
-
u
a
= 50 kPa
b
= 12 °
= 100 kPa
3
600
= 150 kPa
3
= 200 kPa
3
500
= 250 kPa
3
b
= 32 °
= 300 kPa
Inflection
400
300
200
100
Inflection
0
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
Matric suction (
u
a
-
u
w
), kPa
Figure 11.72
Intersection line between failure envelope and the
τ
f
versus matric suction plane.
40
σ
3
-
u
a
= 300 kPa
30
σ
3
-
u
a
= 250 kPa
σ
3
-
u
a
= 200 kPa
σ
3
-
u
a
= 50 kPa
20
σ
3
-
u
a
= 100 kPa
σ
3
-
u
a
= 150 kPa
10
0
0
100
200
300
Matric suction (
u
a
-
u
w
), kPa
Figure 11.73
Nonlinearity in relationship between
φ
b
and matric suction for constant-water-













































Search WWH ::

Custom Search