Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
120
400
350
100
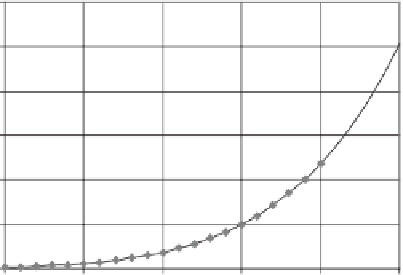
Lowe (1977)
Tetens (1930)
300
Tetens(1930)
Lowe(1977)
80
250
60
200
40
150
20
100
0
50
0
20
40
60
80
100
0
Temperature,°C
0
20
40
60
80
100
Figure 6.29
Curve of saturation vapor pressure versus tempera-
ture.
Temperature,°C
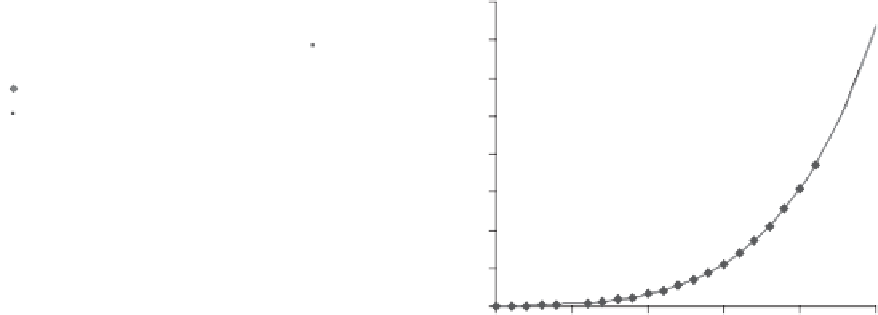
Figure 6.30
Slope of saturation vapor pressure versus tempera-
ture relationship.
6.3.11 Calculation of Slope of Saturation Vapor
Pressure versus Temperature Curve,
The Tetens (1930) equation for calculating the slope of the
saturation vapor pressure versus temperature curve is as fol-
lows:
ε
=
ratio of molecular weight of water vapor to dry air
equal to 0.622, and
L
v
=
latent heat of vaporization, MJ/kg.
At standard atmospheric pressure conditions (i.e.,
101.3 kPa) and a temperature of 20
◦
C, the psychrometric
constant is equal to 0.06733 kPa/
◦
C.
4098
u
air
v
0
=
(6.28)
T
a
+
237
.
3
2
where:
6.3.13 Calculation of Latent Heat of Vaporization,
L
v
Latent heat of vaporization,
L
v
, varies with temperature in
accordance with the following equation (Harrison, 1963):
=
slope of the saturation vapor pressure versus tem-
perature, kPa/
◦
C,
air temperature,
◦
C, and
T
a
=
u
air
v
0
=
saturation vapor pressure, kPa.
L
v
=
2
.
501
−
0
.
002361
T
a
(6.30)
The Tetens (1930) equation (i.e., Eq. 6.28) can also be
used with the saturation vapor pressures calculated using
the Lowe (1977) equation (i.e., Eq. 6.27) to calculate the
slope of the saturation vapor pressure versus temperature
curve. The results from the Tetens (1930) equation and the
Lowe (1977) are essentially the same as shown in Fig. 6.30.
where:
L
v
=
latent heat of vaporization, MJ/kg, and
air temperature,
◦
C.
T
a
=
The value of latent heat varies only slightly over normal
temperature ranges. A value of 2.45 MJ/kg, corresponding
to 20
◦
C, is often used.
6.3.12 Calculation of Psychrometric Constant,
η
The psychrometric constant
η
is not truly a constant since
it varies slightly with elevation but is generally taken as a
constant in the equation relating the standard wet and dry
bulb hygrometer equation. The psychrometric constant can
be calculated as follows:
6.3.14 Calculation of Atmospheric Pressure,
u
a
Absolute atmospheric pressure varies with elevation and
temperature in accordance with the following equation
(Burman et al., 1987):
C
a
¯
u
a
εL
v
T
K
0
−
g/(Rα
1
)
α
1
z
z
0
η
=
(6.29)
−
u
a
=
¯
u
atm
(6.31)
where:
T
K
0
psychrometric constant, kPa/
◦
C,
η
=
where:
specific heat of moist air equal to 1.013 kJ / (kg
◦
C),
C
a
=
u
a
¯
=
absolute atmospheric pressure equal to
(u
atm
+
u
a
)
,
where
u
atm
is standard pressure (sea level) at
101.3 kPa,
u
a
¯
=
absolute atmospheric pressure at elevation,
z
, kPa,
u
atm
=
atmospheric pressure at
sea level,
taken as
101.3 kPa,
























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search