Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
35
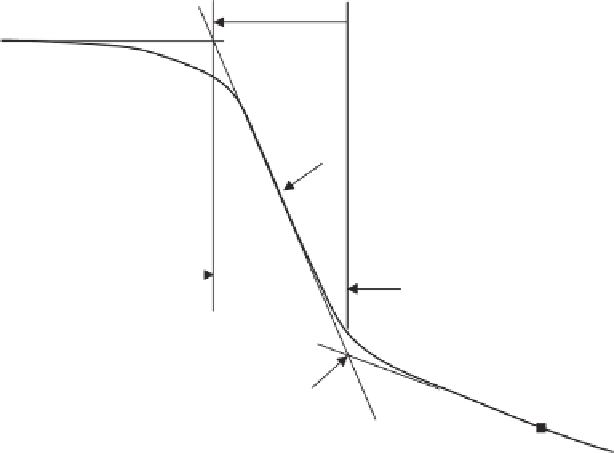
Transition
zone
30
Air-entry
value
25
Inflection point
20
15
Boundary
effect zone
Residual zone
10
5
Residual
conditions
0
10
6
0.1
1
10
100
1000
10,000
100,000
Soil suction, kPa
Figure 5.6
Typical desorption SWCC showing distinct zones of desaturation.
viewed as a part of the water content constitutive surface
for the overall volume-mass constitutive relationships, as
shown in Figs. 5.4 and 5.5.
The SWCC is broadly defined as the relationship between
the amount of water in a soil and soil suction. This simplis-
tic definition means that the term SWCC refers to a class
of relationships and immediately gives rise to a number of
questions:
of water in the soil are (i) gravimetric water content
w
,
(ii) volumetric water content
θ
, (iii) degree of saturation
S,
and (iv) volume of water,
V
w
,
referenced to the original
volume of the specimen,
V
0
(i.e.,
V
w
/V
0
)
.
Gravimetric water content
w
is the most common term
used in geotechnical engineering and is defined as follows:
M
w
M
s
w
=
(5.1)
1. How should the amount of water in the soil be quan-
tified?
2. Are different ways of quantifying the amount of water
used for different estimation procedures?
3. What is the influence of deformation (or overall volume
change) on the interpretation of the data for geotechnical
engineering applications?
4. What influence does “initialization of stresses” at the
start of the SWCC test have on the interpretation of test
data? For example, the test results from an initial slurry
soil specimen is quite different from a compacted or
undisturbed soil specimen.
5. What component(s) of soil suction are plotted on the
SWCC?
6. How is the hysteresis of the SWCC taken into account
for various geotechnical engineering applications?
7. What is the primary SWCC information that is used
when solving geotechnical engineering problems?
where:
w
=
gravimetric water content,
M
w
=
mass of water, and
M
s
=
mass of soil solids.
Volumetric water content
θ
is commonly used in
agriculture-related disciplines and relates the amount of
water in the soil to the total volume of the soil:
V
w
V
v
+
θ
=
(5.2)
V
s
where:
θ
=
volumetric water content,
V
w
=
volume of water,
V
v
=
volume of voids, and
V
s
=
volume of solids.
5.2.1 Designation of Amount of Water in Soil
The SWCC defines the amount of water in a soil versus soil
suction. The amount of water in the soil can be defined using
more than one variable. Variables used to define the amount
It is difficult to measure the total volume of the soil speci-
men when testing an unsaturated soil. It is easier to reference
the amount of water in the soil to the original volume of the



























Search WWH ::

Custom Search