Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
0.67
2.5
0.62375
0.5775
0.53125
0.485
0.43875
0.3925
0.34625
0.3
0.67
0.62375
2.5
2
0.5775
0.53125
0.485
0.43875
0.3925
0.34625
1.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
1
0.5
0
0.3
0
(a)
(a)
0.3
0.25
0.2
0.15
0.1
0.05
0
0.3
0.25
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.2
0.15
0.1
0.05
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0
(b)
(b)
1.25
1
0.75
0.5
0.25
0
1.25
1
1.25
0.75
0.5
0.25
1.25
1
0.75
1
0.5
0.75
0
0.25
0.5
0.25
0
(c)
0
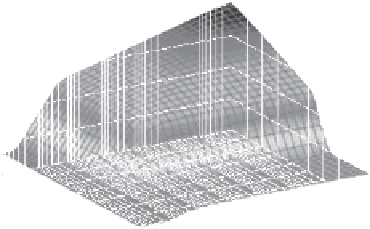
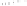
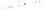
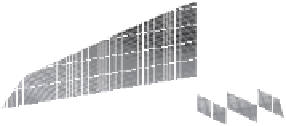
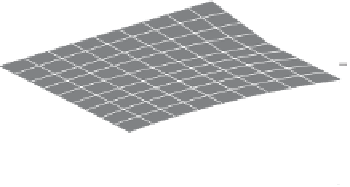
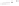
Figure 5.5
Volume-mass constitutive surfaces for sand soil (from
Pham, 2005a): (a) void ratio constitutive surface, (b) gravimet-
ric water content constitutive surface, and (c) degree-of-saturation
constitutive surface.
(c)
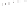
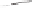
Figure 5.4
Volume-mass constitutive surfaces for highly plas-
tic clay preconsolidated to 200 kPa (from Pham, 2005a): (a) void
ratio constitutive surface, (b) gravimetric water content constitutive
surface, and (c) degree-of-saturation constitutive surface.
air flow, and heat flow problems involving unsaturated soils
(Fredlund, 1997a; M.D. Fredlund, 2000). The permeability
function and the water storage function for an unsaturated
soil are related to the SWCC. In each case, it is impor-
tant that the proper form of the SWCC be used to estimate
the unsaturated soil properties. The form of the SWCC that
should be used depends upon whether or not the soil under-
goes volume change as soil suction is changed.
The unsaturated soil property functions are estimated
using the SWCC and the saturated soil properties. The
SWCC becomes the single most valuable piece of soil
information for geotechnical engineering practice involving
unsaturated soils. It is necessary that the SWCC be properly
estimated (or measured) and interpreted. The SWCC can be
saturation versus soil suction plot and subdivide the SWCC
into the “boundary effect” zone, the “transition” zone, and
the “residual” zone. The same three zones of desaturation
can be defined for the drying (or desorption) branch and the
wetting (or adsorption) branch.
5.2 VOLUME-MASS CONSTITUTIVE RELATIONS
The SWCC constitutes the primary soil information required
for the analysis of seepage, shear strength, volume change,


































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































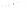
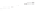




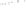








































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































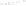























































































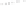















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search