Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
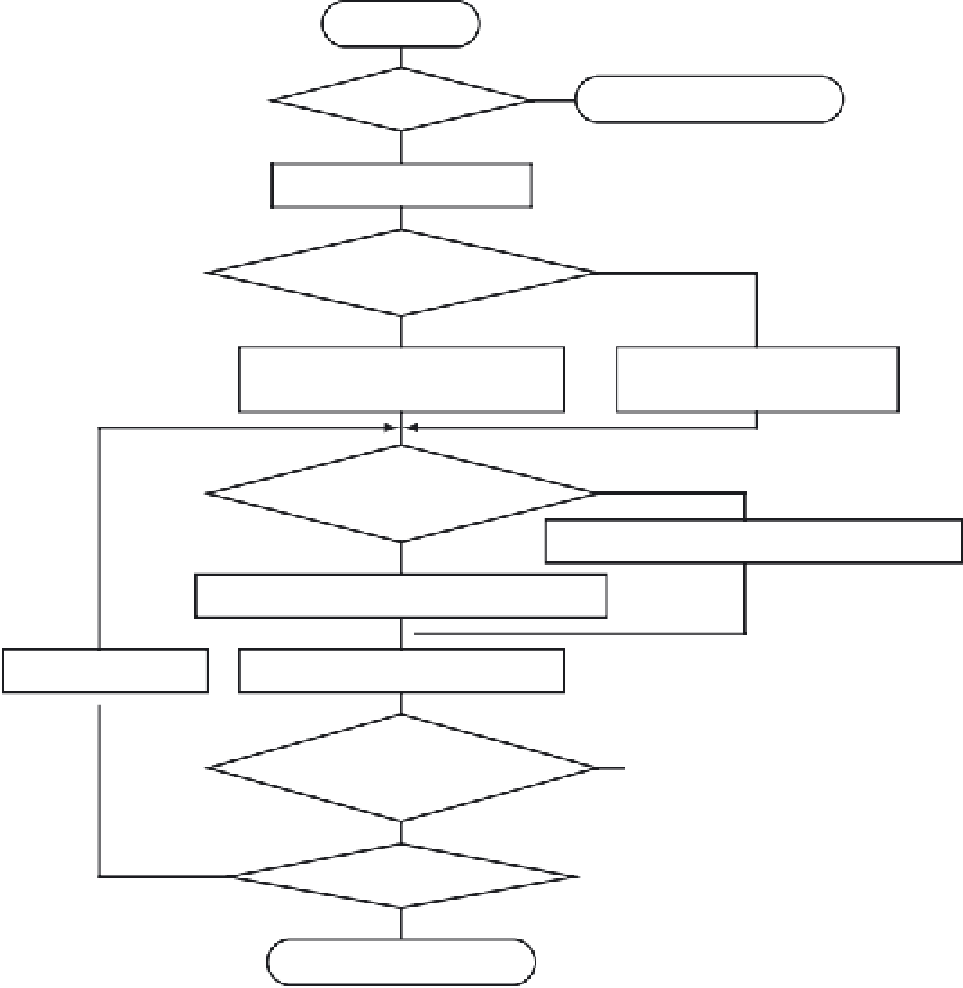
Start
No
Program/erase impossible
T
bus
≤ 1
μ
s?
Ye s
PRDIV8 = 0
No
oscillator clock > 12.8 MHz?
Ye s
PRDIV8 = 1
PRDCLK = oscillator clock/8
PRDCLK = oscillator clock
No
PRDCLK[MHz] × (5 +
T
bus
[
μ
s])
an integer?
FDIV[5:0] = INT(PRDCLK[MHz] × (5 +
T
bus
[
μ
s]))
Ye s
FDIV[5:0] = PRDCLK[MHz] × (5 +
T
bus
[ms]) - 1
Try to decrease
T
bus
FCLK = PRDCLK/(1 + FDIV[5:0])
Ye s
1/FCLK[MHz] +
T
bus
[
μ
s]
≥
5
and FCLK
≥
0.15MHz?
END
No
Ye s
FDIV[5:0]
≥
4?
No
Program/erase impossible
Figure 14.16
■
PRDIV8 and FDIV bits determination procedure
command write sequence can be started. The following three-step procedure should be strictly
adhered to when programming or erasing the flash memory:
Step 1
Write the aligned data word to be programmed to the valid flash address space. The address
and data will be stored in internal buffers. For programming, all address bits are valid. For
flash memory erasure, the value of the data bytes is “don't care.” For bulk erasure, the
address can be anywhere in the available address space of the block to be erased. For sector
erasure, the address bits 7 to 0 are ignored for the flash. A sector has 256 bytes.



Search WWH ::

Custom Search