Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
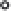
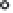
R
f
R
1
V
IN
+12 V
-
R
R
f
R
f
V
OUT
= -
V
IN
-
V
1
74 1
(12.3)
V
1
R
2
+
R
2
- 12 V
(a) Summing circuit
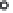
R
0
R
0
+12 V
V
IN
-
V
IN
V
OUT
=
-
(12.4)
74 1
+
- 12 V
(b) Inverting voltage follower
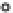
R
0
R
f
R
0
+12 V
V
IN
-
+12 V
R
1
-
741
V
M
741
+
V
OUT
+
R
2
- 12 V
- 12 V
V
M
= -
V
IN
V
1
R
f
R
f
V
IN
-
V
1
(12.5)
V
OUT
=
R
1
R
2
(c) Level shifter and scaler
Figure 12.7
■
Level shifting and scaling circuit
The block diagram of the HCS12 A/D converter (ADC) is shown in Figure 12.8. An HCS12
microcontroller may have one or two 8-channel, 10-bit A/D converters. With a 2-MHz conver-
sion clock, the ADC can perform an 8-bit single conversion in 6 µs or a 10-bit single conversion
in 7 µs. An A/D conversion sequence can be started by writing into a register or by a valid signal
on an external trigger input. The ADC uses the successive-approximation method to perform the
conversion.
The HCS12 uses two 8-bit registers to hold a conversion result. The result can be stored
either right- or left-justified. The A/D conversion is performed in a sequence from one to eight



















Search WWH ::

Custom Search