Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
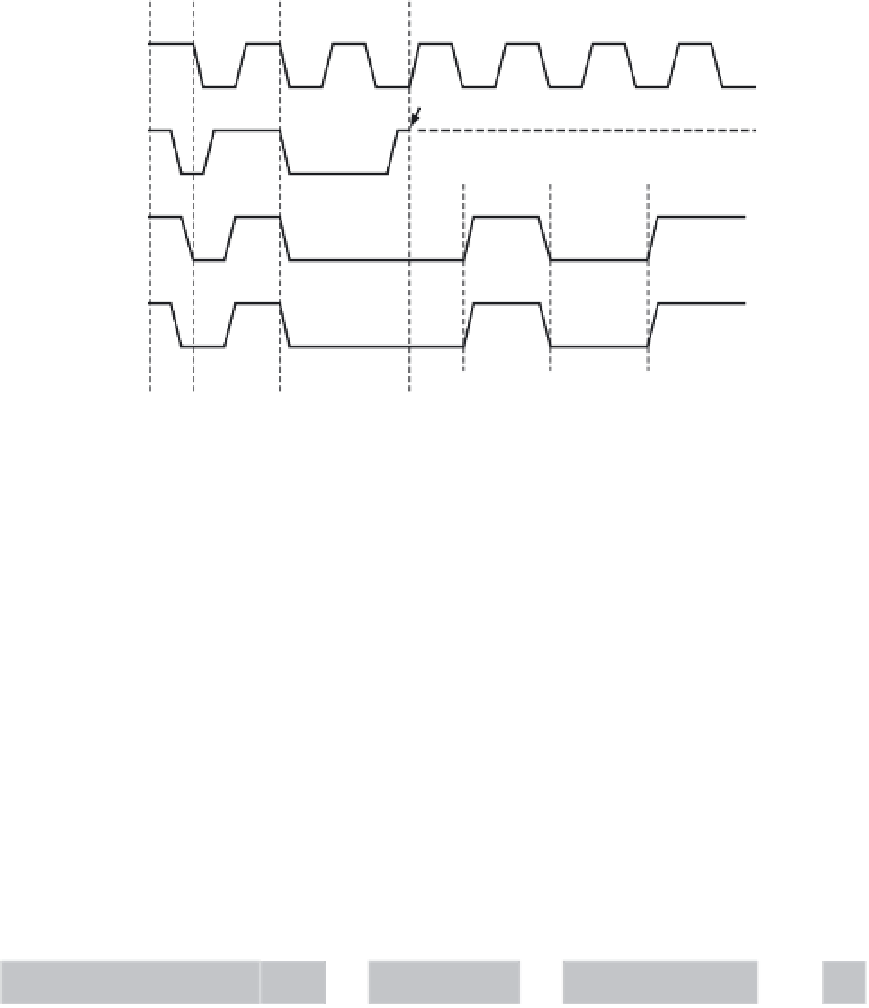
SCL
Master 1 loses arbitration
Data1
≠
SDA
Data1
Data2
SDA
Figure 11.9
■
Arbitration procedure of two masters
I
2
C allows a master device to use either the 7-bit or the 10-bit address to specify a slave de-
vice for data transfer. The following are the possible I
2
C data transfer formats:
•
Master transmitter to slave receiver
. The transfer direction is not changed. An
example of this format using the 7-bit addressing is shown in Figure 11.10.
•
Master reads slave immediately after the first byte (address byte)
. At the moment
of the first acknowledgement, the master transmitter becomes a master receiver
and the slave receiver becomes a slave transmitter. The first acknowledgement is
still generated by the slave. The stop condition is generated by the master, which
has previously sent a negative acknowledgement (A). An example of this format
using the 7-bit addressing is shown in Figure 11.11.
•
Combined format
. During a change of direction within a transfer, both the start
condition and the slave address are repeated, but with the R/W bit reversed. If a
master receiver sends a repeated start condition, it has previously sent a negative
acknowledgement. An example of this format in the 7-bit addressing is shown in
Figure 11.12.
S
Slave address
A
Data
A
Data
P
R/W
A/A
Data transferred
(
n
bytes + acknowledge)
0 (write)
From master to slave
A
= acknowledge (SDA low)
A = not acknowledge (SDA high)
S = start condition
P = stop condition
From slave to master
Figure 11.10
■
A master transmitter addressing a slave receiver with a 7-bit address. The
transfer direction is not changed















Search WWH ::

Custom Search