Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
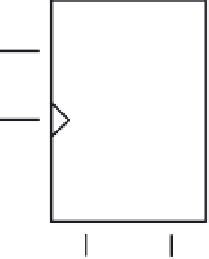
D
Q
CLK
Set
Reset
Figure 1.3
■
Block diagram of a D flip-flop with a set and reset
•
The Q signals of all the flip-flops of the program counter determine the address of
the next instruction to be fetched.
•
The set and reset inputs are active low (low voltage means logic 1) and ca
nnot
be
low at the same time. When set is low, the Q signal is forced to 1. When reset is
low, the Q signal is forced to 0.
As described in Section 1.3.1, a microprocessor or microcontroller has instructions to
change the program flow. The design of the program counter circuit must take this into account.
Figure 1.4 shows the block diagram of a program counter of an 8-bit microcontroller that allows
the program counter to be
•
Forced to 0
•
Incremented by 1
•
Incremented by a field in the IR
•
Loaded with a jump target
1
Branch
offset
01
MUX1
Branch
16
Adder
Q
s
16
CLK
Clk
16
D
s
Jump
target
16
Power
on
Reset
Jump
Figure 1.4
■
A simplified block diagram of the program counter (PC) of an 8-bit microcontroller



















Search WWH ::

Custom Search