Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
FIGURE 12.
FIGURE 11.
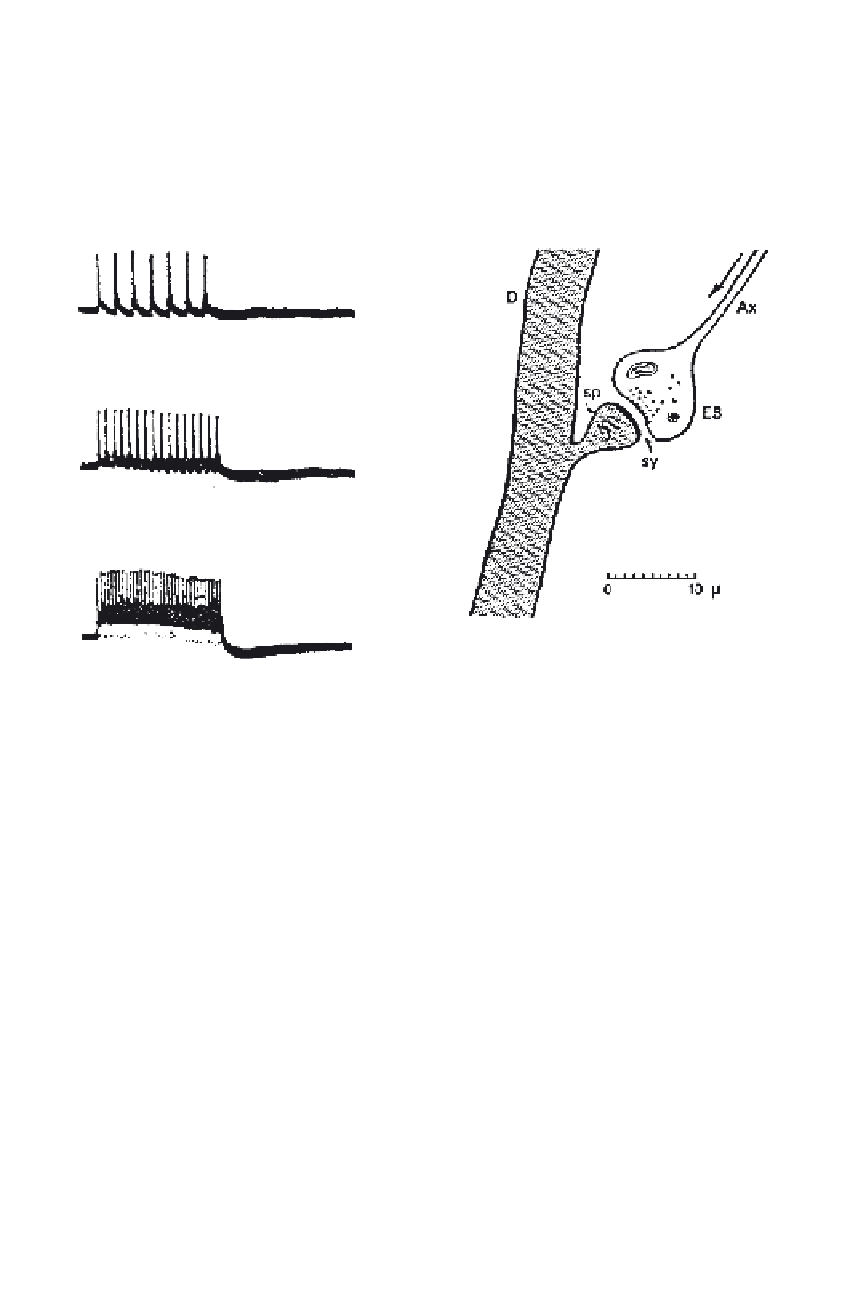
Synapse
Figure 12 sketches a synaptic junction. The afferent axon (Ax), along which
the pulses travel, terminates in an end bulb (EB), which is separated from
the spine (sp) of a dendrite (D) of the target neuron by a minute gap (sy),
the “synaptic gap.” (Note the many spines that cause the rugged appear-
ance of the dendrites in Fig. 10). The chemical composition of the “trans-
mitter substances”filling the synaptic gap is crucial in determining the effect
an arriving pulse may have on the ultimate response of the neuron: Under
certain circumstances it may produce an “inhibitory effect” (cancellation of
Search WWH ::

Custom Search