Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
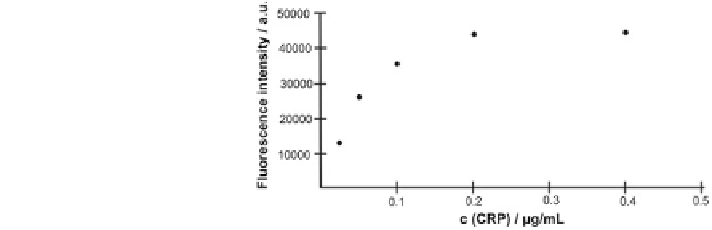
Fig. 6 Concentration
dependency of CRP in a
miniaturized microarray
format
assay, and the choice of detection method. In addition, the processing of the assay
within the chip has to be optimized. Here, incubation times and flow rates can be
varied for an effective optimization of the assay.
As an example, the detection of C-reactive protein (CRP) by means of a
common antibody assay and the optical read-out will be described. CRP is an acute
phase protein and its level arises due to inflammation.
As a first step the substrate has to be modified to enable a covalent binding of
the capture antibody to the surface. In this experiment, surface modification using
3-glycidyloxyproyltriethoxysilane was chosen. On that surface, the capture anti-
body was deposited by contact-free spotting techniques. For CRP detection a
monoclonal mouse anti-CRP-antibody was used. The monoclonal antibody was
chosen to be as specific as possible in the first reaction step avoiding cross-
reactivity with other inflammation markers. Besides the capture antibody also
marker spots (containing just the labeled detector antibody) and negative control
spots containing just the spotting buffer were deposited onto the substrate. Prior to
incubation with CRP the surface was blocked with an appropriate blocking agent,
in this case 3 % bovine serum albumin. After incubation of the CRP and different
washing steps a polyclonal rabbit anti-CRP-antibody was used as a secondary
antibody. This is able to bind from the opposite side of the CRP. For the last step a
polyclonal goat anti-rabbit-antibody labeled with Cy5 was chosen to make the
optical detection of the bound analyte possible. Choosing in both cases a poly-
clonal antibody leads to signal amplification because more than one antibody is
able to bind to the same target. The microarray was optimized to show its use as a
diagnostic tool. In Fig.
6
the concentration dependency is shown from 50 to
400 ng/mL.
To optimize the microarray different washing solutions (maybe with use of
detergents) and a variety of different blocking agents can be used. Besides these
optimization steps also the number of washing steps and the incubation time can
be varied. In the context of the Lab-on-Chip system incubation times can be
controlled by the flow rate.
A typical flow protocol for an immunoassay within the ivD-platform includes
different washing and incubation steps. As a first step, PBS buffer is pumped over
the sensor field to wet the microfluidic channels. Then the sample is rinsed over the
microarray followed by washing steps and the application of the secondary and