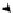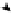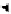Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
the poverty headcount for Eastern Asia has declined markedly since
1990, to its present level of less than 16 per cent, having stood as high
as 60 per cent in 1990.
A specific measure of some of the wider aspects of multidimensional
poverty is provided by the Human Poverty Index (HPI),
developed by
the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) as an extension
of the HDI since the 1990s and used through to 2010. Accordingly, the
HPI concentrated on measuring deprivation with respect to the three
essential elements used to assess the original HDI: a long and healthy
life, knowledge and a decent standard of living (see Figure 1.4.1).
First, the health dimension was measured by the probability at birth
of not surviving to 40 years of age. Secondly, education was measured
by the adult literacy rate. Thirdly, the income component was measured
A
HPI-1
A long and
healthy life
Probability at birth
of not surviving
to age 40
DIMENSION
Knowledge
A decent standard of living
INDICATOR
Adult rate
illiteracy
Percentage of population
not using an improved
water source
Percentage of children
under weight-for-age
48
Deprivation in
a decent standard of living
Human poverty index
for developing countries (HPI-1)
B
HPI-2
DIMENSION
A long and
healthy life
Probability at birth
of not surviving
to age 60
A decent standard
of living
Knowledge
Social exclusion
INDICATOR
Percentage of adults
lacking functional
literacy skills
Percentage of people
living below the
poverty line
Long-term
unemployment rate
Human poverty index
for selected OECD countries (HPI-2)
Figure 1.4.1
Calculating (A) the Human Poverty Index 1 (HPI-1) and
(B) Human Poverty Index 2 (HPI-2)