Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
economic growth. During the era of unilinear development models
and theories, the growth of GDP/GNP was taken as the surrogate
measure of development. More accurately, in this approach the stan-
dard of living of a country is used as a summary measure of develop-
ment (Thirlwall, 2008). The GDP/GNP of a territory is directly affected
both by the number of people working within a country and their
overall level of productivity.
•
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita
- measures the value
of all goods and services produced by a nation or a territory, whether
by national or foreign companies. When calculated, the national
total is divided by the total population, to give the value of goods and
services produced per head of the population.
•
Gross National Product (GNP) per capita
- this is Gross
Domestic Product to which net income derived from overseas is
added. In other words, income which is generated abroad is added,
and payments made overseas are subtracted. This total is also then
divided by the total population. In recent years, international orga-
nizations like the World Bank have increasingly referred to this as
Gross National Income (GNI) per capita.
28
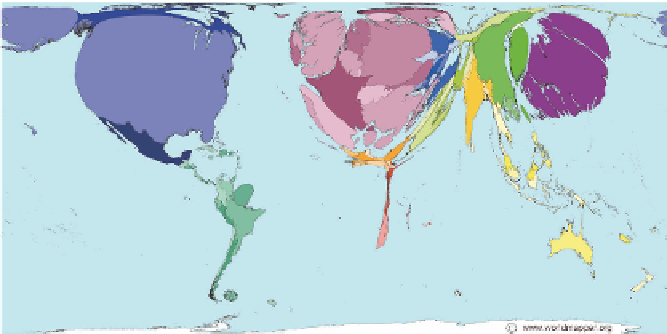
Through time from the 1950s, GDP, GNP/GNI have been used as mea-
sures of development. Figure 1.2.1 shows the global distribution of GDP
Figure 1.2.1
Gross Domestic Product by country (size of country shows the
proportion of world wealth accounted for by that country).
Source
: Worldmapper map number 169 © Copyright SASI Group (University of Sheffield)