Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
Z
radar
θ
-b/2
b/2
Y
ϕ
a
X
Figure 11.28. Coordinates for a perfectly conducting isosceles triangular plate.
4π
A
2
λ
2
)
4
)
2
(
sin
α
(
sin
2α
2α
)
2
-------------
σ
=
(
cos
θ
------------------
+
-----------------------------------
(11.66)
α
4
4α
4
and for incidence in the plane
ϕπ2
=
⁄
4π
A
2
λ
2
)
4
(
sin
(
β 2
⁄
)
)
2
-------------
------------------------------
σ
=
(
cos
θ
(11.67)
)
4
(
β 2
⁄
Fig. 11.29
shows a plot for the normalized backscattered RCS from a per-
fectly conducting isosceles triangular flat plate. In this example
,
. This plot can be reproduced using MATLAB function
Ðrcs_isosceles.mÑ
given in Listing 11.11 in Section 11.9.
a
=
0.2
m
b
=
0.75
m
MATLAB Function Ðrcs_isosceles.mÑ
The function
Ðrcs_isosceles.mÑ
calculates and plots the backscattered RCS
of a triangular flat plate. Its syntax is as follows:
[rcs] = rcs_isosceles (a, b, freq, phi)
where
Symbol
Description
Units
Status
a
height of plate
meters
input
b
base of plate
meters
input
freq
frequency
Hz
input
phi
roll angle
degrees
input
rcs
array of RCS versus aspect angle
dBsm
output
































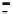
Search WWH ::

Custom Search