Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
11.5.6. Rectangular Flat Plate
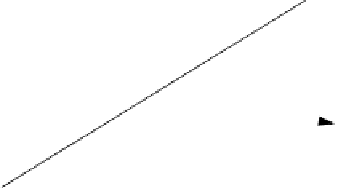
Consider a perfectly conducting rectangular thin flat plate in the x-y plane as
shown in
Fig. 11.26
.
The two sides of the plate are denoted by and . For
a linearly polarized incident wave in the x-z plane, the horizontal and vertical
backscattered RCS are, respectively, given by
2
a
2
b
b
2
-----
σ
1
V
σ
2
V
4
2
1
σ
5
1
--------
σ
3
V
σ
V
=
σ
2
V
------------
+
(
+
σ
4
V
)
(11.50)
cos
θ
b
2
π
2
σ
2
H
4
1
) σ
5
1
σ
H
=
----- σ
1
H
σ
2
H
------------
---------
(
σ
3
H
+
σ
4
H
(11.51)
cos
θ
where
k
=
2πλ
⁄
and
sin
(
k
asin
θ
)
-----------------------------
)
∗
σ
1
V
=
cos
(
k
asin
θ
)
j
=
(
σ
1
H
(11.52)
sin
θ
e
jka
π 4
(
⁄
)
σ
2
V
=
-----------------------------
(11.53)
2π
k
(
32
⁄
jk
asin
θ
(
1
+
sin
θ
)
e
σ
3
V
=
--------------------------------------------
(11.54)
)
2
(
1
sin
θ
)
e
jk
asin
θ
(
1
sin
θ
σ
4
V
=
-----------------------------------------
(11.55)
)
2
(
1
+
sin
θ
Z
radar
θ
-a
-b
b
Y
a
X
Figure 11.26. Rectangular flat plate.



















Search WWH ::

Custom Search