Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
σ
0
m
2
m
2
where is the clutter scattering coefficient, a dimensionless quan-
tity that is often expressed in dB. Some radar engineers express
(
⁄
)
σ
0
in terms of
σ
0
squared centimeters per squared meter. In these cases,
is
40
dB
higher than
normal.
6.2. Surface Clutter
Surface clutter includes both land and sea clutter, and is often called area
clutter. Area clutter manifests itself in airborne radars in the look-down mode.
It is also a major concern for ground-based radars when searching for targets at
low grazing angles. The grazing angle is the angle from the surface of the
earth to the main axis of the illuminating beam, as illustrated in Fig. 6.1.
ψ
g
ψ
g
earth surface
Figure 6.1. Definition of grazing angle.
Three factors affect the amount of clutter in the radar beam. They are the
grazing angle, surface roughness, and the radar wavelength. Typically, the clut-
ter scattering coefficient is larger for smaller wavelengths. Fig. 6.2 shows a
sketch describing the dependency of on the grazing angle. Three regions
are identified; they are the low grazing angle region, flat or plateau region, and
the high grazing angle region.
σ
0
σ
0
σ
0
dB
low grazing
angle region
high grazing
angle region
plateau region
0
dB
grazing angle
critical angle
>
60°
Figure 6.2. Clutter regions.











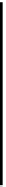


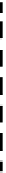











Search WWH ::

Custom Search