Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
2.9.1. Cell-Averaging CFAR (Single Pulse)
on a series of range and/or Doppler bins (cells). The echo return for each pulse
is detected by a square law detector. In analog implementation these cells are
obtained from a tapped delay line. The Cell Under Test (CUT) is the central
cell. The immediate neighbors of the CUT are excluded from the averaging
process due to a possible spillover from the CUT. The output of reference
cells ( on each side of the CUT) is averaged. The threshold value is
obtained by multiplying the averaged estimate from all reference cells by a
constant
M
M
⁄
2
K
0
(used for scaling). A detection is declared in the CUT if
Y
1
≥
K
0
Z
(2.101)
Cell-averaging CFAR assumes that the target of interest is in the CUT and all
reference cells contain zero mean independent Gaussian noise of variance .
Therefore, the output of the reference cells, , represents a random variable
with gamma probability density function (special case of the Chi-square) with
degrees of freedom. In this case, the gamma
pdf
is
ψ
2
Z
2
M
2ψ
2
(
z
⁄
)
(
M
⁄
2
)
1
z
e
f
()
=
--------------------------------------------
;
z
>
0
(2.102)
2
M
⁄
2
ψ
M
Γ
M
(
⁄
2
)
reference
cells
guard
cells
guard
reference
cells
CUT
cells
…
…
input
square law
detector
M
⁄
2
M
⁄
2
…
Σ
Σ
Σ
Y
1
Z
K
0
Z
K
0
comparator
threshold
output
Figure 2.18. Conventional CA-CFAR.
The probability of false alarm corresponding to a fixed threshold was
derived earlier. When CA-CFAR is implemented, then the probability of false





































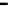














Search WWH ::

Custom Search