Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
P
J
J
1
1
2
P
2
J
4
J
J
5
3
8 0 2
t
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
t = 17
(a)
c
P
J
1
J
1
2
P
J
J
J
5
2
3
4
t
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
t = 22
(b)
c
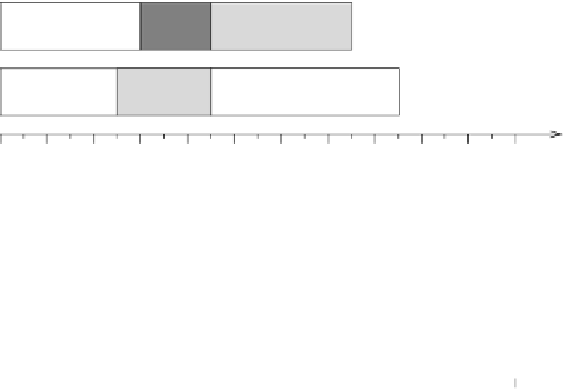
Figure 2.23
share the same
resource in exclusive mode, the optimal schedule length (a) increases if the computation
time of job
J
1
Example of anomaly under resource constraints. If
J
2
and
J
4
is reduced (b). Jobs are statically allocated on the processors.
ANOMALIES UNDER RESOURCE CONSTRAINTS
The following example shows that, in the presence of shared resources, the schedule
length of a task set can increase when reducing tasks' computation times. Consider
the case illustrated in Figure 2.23, where five jobs are statically allocated on two pro-
cessors: jobs
J
1
and
J
2
on processor P1, and jobs
J
3
,
J
4
and
J
5
on processor P2 (jobs
are indexed by decreasing priority). Moreover, jobs
J
2
and
J
4
share the same resource
in exclusive mode; hence their execution cannot overlap in time. A schedule of this
task set is shown in Figure 2.23a, where the total completion time is
t
c
=17.
If we now reduce the computation time of job
J
1
on the first processor, then
J
2
can be-
gin earlier and take the resource before
J
4
. As a consequence, job
J
4
must now block
over the shared resource and possibly miss its deadline. This situation is illustrated in
Figure 2.23b. As we can see, the blocking time experienced by
J
4
causes a delay in
the execution of
J
5
(which may also miss its deadline), increasing the total completion
time of the task set from 17 to 22.
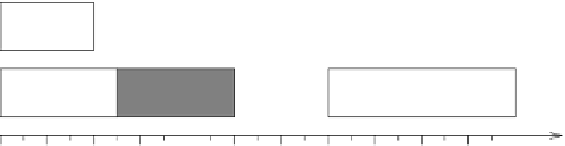
Search WWH ::

Custom Search