Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
Z
k
(
t
)
α
k
t
Δ
k
0
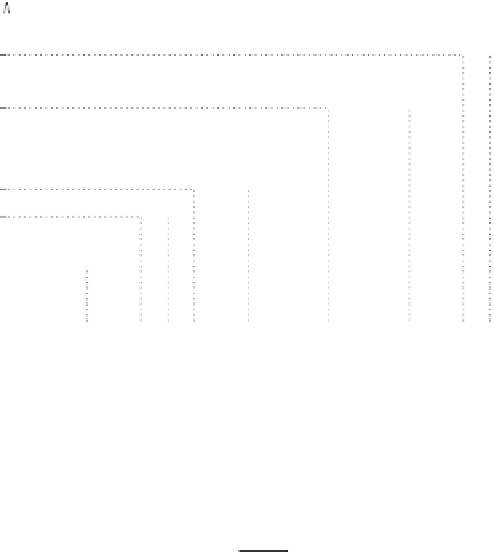
Figure 9.19
A reservation implemented by a static partition of intervals.
In general, for a given supply function
Z
k
(
t
), the bandwidth
α
k
and the delay Δ
k
can
be formally defined as follows:
Z
k
(
t
)
t
α
k
=
lim
t→∞
(9.14)
t
.
Z
k
(
t
)
α
k
Δ
k
=sup
t≥
0
−
(9.15)
If a reservation is implemented using a periodic server with unspecified priority that
allocates a budget
Q
k
every period
T
k
, then the supply function is the one illustrated
in Figure 9.20, where
α
k
=
Q
k
/T
k
(9.16)
Δ
k
=2
T
k
−
Q
k
)
.
(9.17)
It is worth observing that reservations with smaller delays are able to serve tasks with
shorter deadlines, providing better responsiveness. However, small delays can only
be achieved with servers with a small period, condition for which the context switch
overhead cannot be neglected. If
σ
is the runtime overhead due to a context switch
(subtracted from the budget every period), then the effective bandwidth of reservation
is
=
α
k
1
.
Q
−
σ
σ
Q
k
α
e
k
−
=
T
k







Search WWH ::

Custom Search