Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
J
1
J
2
J
3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
ρ
(t)
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
t
0.0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
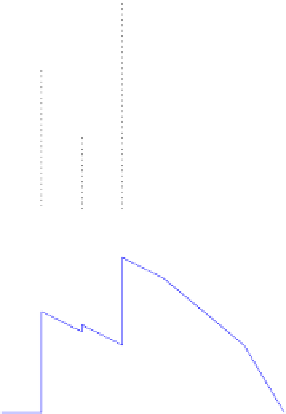
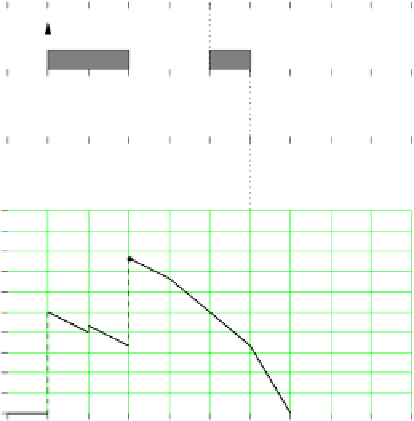
Figure 9.2
Instantaneous load as a function of time for a set of three real-time jobs.
Note that while the overload is a condition related to the processor, the overrun is a
condition related to a task (or a single job). A task overrun does not necessarily cause
an overload. However, a large unexpected overrun or a sequence of overruns can cause
very unpredictable effects on the system, if not properly handled. In the following, we
distinguish between two types of overload conditions:
Transient overload
: it is an overload condition occurring for a limited duration,
in a system in which the average load is less than or equal to one (
ρ
≤
1), but the
maximum load is greater than one (
ρ
max
>
1).
Permanent overload
: it is an overload condition occurring for an unpredictable
duration, in a system in which the average load is higher than one (
ρ>
1).
In a real-time computing system, a transient overload can be caused by a sequence of
overruns, or by a bursty arrival of aperiodic requests, whereas a permanent overload
condition typically occurs in periodic task systems when the total processor utilization
exceeds one.






















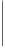



Search WWH ::

Custom Search