Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
1
PE
DS
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
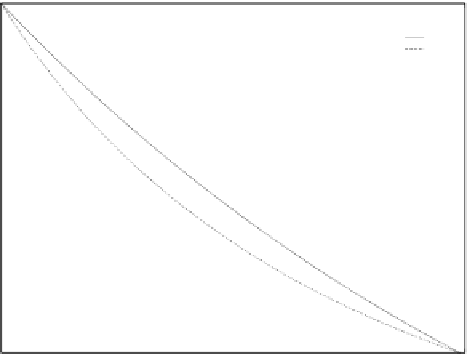
Periodic Utilization factor Up
Figure 5.16
Maximum server utilization as a function of the periodic load.
for PE is 10%, whereas DS utilization cannot be greater than 7%. If instead
U
p
=0
.
3,
PE can have 48% utilization, while DS cannot go over 38%. The performance of the
two algorithms in terms of average aperiodic response times is shown in Section 5.9.
As far as firm aperiodic tasks are concerned, the schedulability analysis under PE is
much more complex than under DS. This is due to the fact that, in general, when an
aperiodic request is handled by the PE algorithm, the server capacity can be distributed
among
n
+1priority levels. Hence, calculating the finishing time of the request might
require the construction of the schedule for all the periodic tasks up to the aperiodic
deadline.
5.6
SPORADIC SERVER
The
Sporadic Server
(SS) algorithm is another technique, proposed by Sprunt, Sha,
and Lehoczky [SSL89], which allows the enhancement of the average response time
of aperiodic tasks without degrading the utilization bound of the periodic task set.
The SS algorithm creates a high-priority task for servicing aperiodic requests and, like
DS, preserves the server capacity at its high-priority level until an aperiodic request
occurs. However, SS differs from DS in the way it replenishes its capacity. Whereas
DS and PE periodically replenish their capacity to full value at the beginning of each












Search WWH ::

Custom Search