Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2.5
Adjoint functions
g
ij
0.015
r
j
,
)
corresponding to zone
=
g
i
(
t
ʩ
3
0.0125
(
when they are
restricted to the optimal
discharge points
r
j
(
i
=
3
)
g
33
0.01
j
=
1
,
2
,
3
)
0.0075
0.005
0.0025
g
31
g
32
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
t
ʳ
i
Table 2.2
Modulation parameters
for the basic discharge rates
Parameter
\
Experiment
1
2
3
4
5
ʳ
1
1
.
0000
1
.
0000
1
.
0000
1
.
0000
1
.
0000
ʳ
2
0
.
9579
0
.
9473
0
.
9789
0
.
8989
0
.
9789
ʳ
3
1
.
0000
1
.
0000
1
.
0000
1
.
0000
1
.
0000
other zones. If it is the case, the application of second stage of the remediation
strategy is necessary to correct the intensity of the basic discharge rates. To this end,
the quadratic programming problem (
2.66
)-(
2.68
) was solved by using the adjoint
functions
g
ij
r
j
,
, the critical concentrations
c
i
given in Table
2.1
and the
corresponding basic discharge rates. Table
2.2
summarizes the optimal modulation
parameters
=
g
i
(
t
)
ʳ
i
obtained for each experiment.
For all the experiments, the slack variables of the quadratic programming prob-
lem (
2.66
)-(
2.68
) are taken equal to zero:
2 and 3), hence,
each critical concentration
c
i
is reached in the respective oil polluted zone exactly.
Table
2.2
shows that the only discharge rate which must be corrected is that located
in zone
ʱ
i
=
ʲ
i
=
0(
i
=
1
,
ʳ
2
1 in the five experiments). This is a consequence of the impact that
the discharge of nutrient at point
r
1
has on the zone
ʩ
2
(
<
ʩ
2
. The optimal discharge rates
for experiments 1 and 4 are shown in Figs.
2.6
and
2.7
, respectively. As compared
with Fig.
2.6
, the intensity of functions
Q
1
and
Q
3
in Fig.
2.7
has increased. This is
the result of the raise in the critical concentrations from 0
2 (see Table
2.1
.At
the same time, the decrease in the intensity of function
Q
2
in Fig.
2.7
compared to
Fig.
2.6
is explained by the drop in the critical concentration of nutrient from 0
.
8to1
.
.
8to
ʳ
2
(see Table
2.2
).
It should be noted that in all the experiments, the slack variables are not necessary
because the feasible space of problem (
2.66
)-(
2.68
) is nonempty when
.
0
5 and also by the correction of
Q
2
through the parameter
ʱ
i
=
ʲ
i
=
0





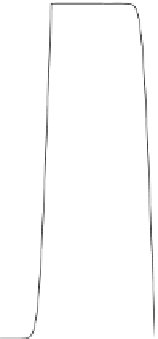


































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search