Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
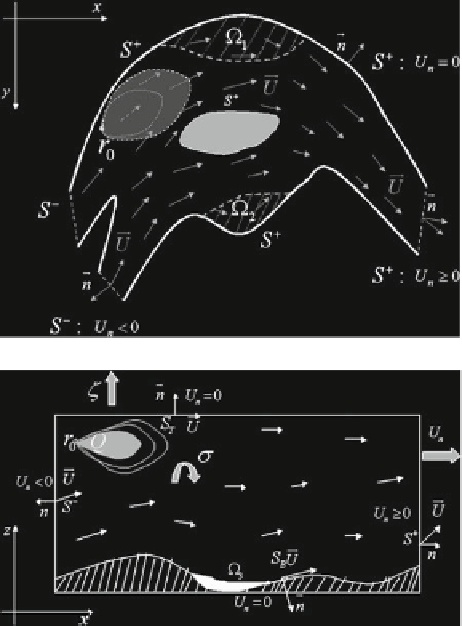
Fig. 2.1
View of domain
D
from above
Fig. 2.2
Cross-sectional
area of domain
D
S
+
∪
S
−
∪
vector to the boundary
∂
D
=
S
T
∪
S
B
of domain
D
,
∂/∂
n
is the derivative
t
is the unit vector directed upward in the
Cartesian coordinate system (Fig.
2.2
). We observe that
in the normal direction, and
k
=
(
0
,
0
,
1
)
0on
S
+
∪
S
−
k
·
n
=
and
U
·
n
=
0on
S
T
∪
S
B
.
(2.12)
Also note that the boundary conditions (
2.6
)-(
2.9
) are general (i.e., not only for
horizontal free and bottom surfaces
S
T
and
S
B
), and hence, the dispersion model can
take into account free surface wave motion and marine topography.
First of all we show that the solution of dispersion model (
2.4
)-(
2.11
) satisfies
the mass balance equation. Indeed, integrating Eq. (
2.4
) over domain
D
we get
∂
∂
D
ˆ
+
·
ˆ
−
∇·
μ
∇
ˆ
+
˃ˆ
+
∇·
ˆ
s
dr
dr
U
dr
dr
dr
t
D
D
D
D
N
=
Q
i
(
t
)ʴ(
r
−
r
i
)
dr
.
i
=
1
D
Search WWH ::

Custom Search