Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
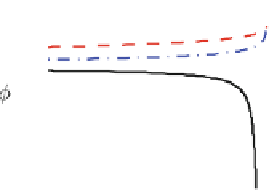
Fig. 4.1
(
top left
) Schematic of the experimental apparatus; (
bottom left
) The thin film of fluid
μ
l
that contains two particle species of equal diameter
d
and variant densities, such that
ˁ
2
>ˁ
1
>ˁ
l
. Two sets of experimental results are shown on the right. In the
bottom right panel
,
as time evolves (images from
left
to
right
), clear fingers form on the flow front, indicating that both
particle species have settled to the channel walls with a clear fluid layer on top that moves ahead.
On the other hand, the particles appear to remain aggregated and well-mixed on the front in the
'ridged' regime, as shown in the
top right panel
ˁ
l
and
of
0.6
0.6
0.4
0.4
0.2
0.2
0
0
0
0.5
1
0
0.5
1
Fig. 4.2
Transition from settled to ridged solutions in
ˆ
for the monodisperse system, for
X
=
1
(
left
)and
X
=
0(
right
). The critical concentrations are
ˆ
c
,
1
=
0
.
459 and
ˆ
c
,
2
=
0
.
521
<ˆ
0
<ˆ
A
): In the settled regime, the heavy particles settle to the
substrate, with a layer of the lighter particles above, and then a clear fluid layer up to
the free surface. The upper bound for the settled region,
Settled
(0
ˆ
A
decreases from
ˆ
c
,
2
to
ˆ
c
,
1
as
X
0
increases from 0 to 1. If
ˆ
0
<ˆ
c
,
1
, then the ODE system guarantees that
ˆ
is monotonically decreasing regardless of
X
0
.






















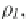

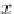







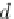















































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search