Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
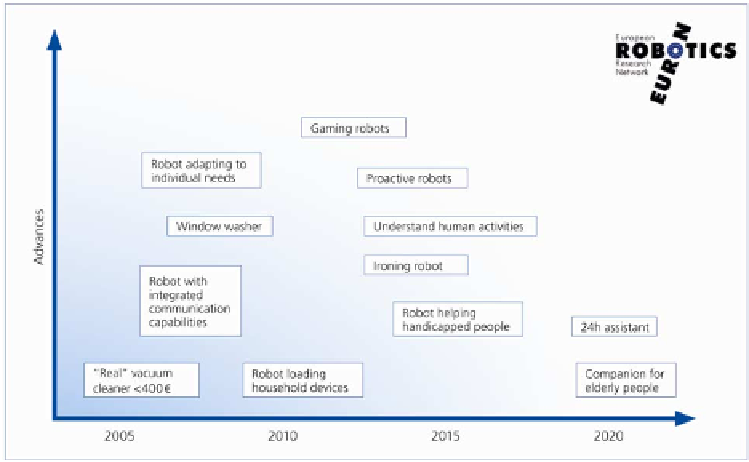
Figure 6.
Adaptive Robot Servants & Intelligent Homes
Ubiquitous Robotics/Network Robots paradigm
Ubiquitous Robotics is a new, emerging paradigm that is related to the fields of
Ambient Intelligence and Ubiquitous/Pervasive Computing. Ubiquitous Robotics arises
from a shift of focus, from information to matter and physicalness: networked,
ubiquitous robotic system will therefore convey data and physical actions, like motion
and forces, in intelligent environments, leading to a profound and pervasive impact on
virtually all new products and at different levels: global, local, “personal”, external and
internal, macro and micro/nano, etc.
By going beyond robotics and mechatronics, and even beyond “traditional” ICT,
the new envisaged scenario will provide far wider application to individual users and to
communities in a broad sense.
An overview of current research in the field of Ubiquitous and Network Robots is
provided in a white paper produced by the EURON Special Interest Group on Good
Experimental Methodology: (Two “Hot Issues” in Cooperative Robotics: Network
Robot Systems, and Formal Models and Methods for Cooperation) (Bonsignorio 2008).
Ubiquitous Robotics in Japan and Korea
The concept of Ubiquitous Robotics first appeared in East Asia, almost simultaneously
in Korea and in Japan; its better name is Network Robots.
The Korean concept of Ubiquitous robot (Ubibot) was introduced in 2004 as the
third generation of robotics. The Ubibot paradigm incorporates three forms of robot:
software robot (Sobot), embedded robot (Embot) and mobile robot (Mobot), which can
provide users with various services by any device through any network, at any place
anytime in a ubiquitous space.
Sobots are virtual robots, which are able to move to any place through a network;
Embots are embedded within the environment or in a Mobot; Mobots provide
integrated mobile services, which are seamless and context-aware.