Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
2.6.3 Physiological preparation
It is now clear that larval lampreys have to be prepared for the non-trophic
phase of metamorphosis. Although not all aspects of the hormonal and
metabolic involvement in this preparation have been identifi ed, the role
of the thyroid axis and lipid metabolism has received the most attention.
Much of what we know about these two parameters of metamorphic
preparation arises from studies of the sea lamprey,
P. marinus
.
These two
areas will receive in depth treatment in this section with data from this
species. Similarity and differences between
P. marinus
and other species
will be highlighted.
2.6.3.1 Lipid metabolism and fat storage
As mentioned above, larva of immediately pre-metamorphic
P. marinus
are heavier than animals of similar length that are unlikely to enter
metamorphosis in that same season. Both morphological and biochemical
evidence have shown that this added weight can be directly correlated with
the deposition of fat (Lowe et al
.
, 1973; O'Boyle and Beamish, 1977; Youson
et
al
.
, 1979; Kao
et al
.
, 1997a,1997b). Immediately pre-metamorphic
P. marinus
and the earliest intervals of metamorphosis show lipogenesis as refl ected
in marked deposits of fat in sites such as the nephric folds of the kidney
(Fig. 2) and increased activity of the enzymes, acetyl-CoA carboxylase and
diacylglycerol acyltransferase (Kao et al
.
, 1997a) compared to animals that
will not metamorphose (Table 1). These lipid stores are primarily in the form
of triacylglycerol (Sheridan and Kao, 1998) and lipolysis will then follow in
later stages of metamorphosis with increases in triacylglycerol lipase activity
in the several sites of lipid deposition (Kao et al
.
, 1997a). Therefore, there are
two phases of lipid metabolism in sea lamprey metamorphosis, lipogenesis
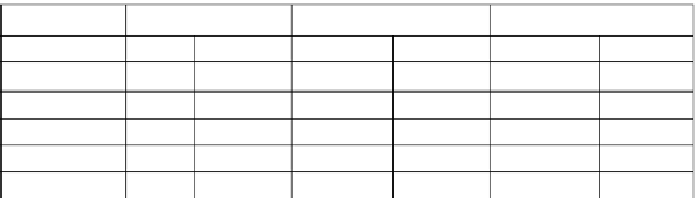
Table 1.
Summary of the features of lipid metabolism in the liver and kidney of
Petromyzon
marinus
during spontaneous and induced metamorphosis and following the blocking of
KClO
4
-inudced metamorphosis with exogenous thyroid hormones (TH-blocked). From
Youson, 2003.
Spontaneous
KClO
4
-induced
TH-blocked
liver
kidney
liver
kidney
liver
kidney
total lipid
↓
↓
↓
↓
↑
↑
lipolysis
↑
↑
↑
↑
↓
↓
lipogenesis
ACC
↓ ↓ ↓
n/d
↑
n/d
DGAT
↓
n/d
↓ ↓
n/d
↑
ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; DGAT, diacylglycerol acyltransferase; ↑ increase; ↓ decrease;
n/d not determined.