Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
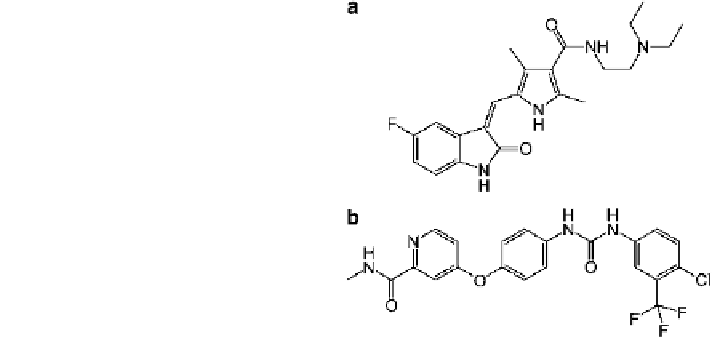
Fig. 4 Chemical structures
of receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitors. a Sunitinib.
b Sorafenib
cannot provide lasting clinical responses. In fact, anti-angiogenic therapy can lead
to heightened invasiveness and increased metastasis of tumors [
72
]. Indeed, a
subset of glioblastoma patients experienced recurrence with more infiltrative
tumors following treatment with bevacizumab [
73
].
4.4 Next-Generation Anti-Angiogenic Agents
A second-generation of anti-angiogenic therapies, the receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor class, is currently under development (Fig.
4
). Unlike bevacizumab, these
drugs are small molecules that inhibit multiple targets; the newer agents can thus
be used as monotherapy for cancer. For example, sunitinib is a receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitor that blocks signaling through VEGF receptors and PDGF
receptors; sunitib also targets other tyrosine kinases including, KIT, FLT3, colony-
stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1), and RET, which are involved in several different
malignancies [
74
]. Sunitinib has been shown to prolong progression-free survival
for renal cell cancer. A multi-center randomized phase III clinical trial was
conducted in 750 patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carci-
noma; patients were randomized to receive either sunitinib or interferon alfa [
75
].
Sunitinib increased progression-free survival by a median time of 6 months as
compared to interferon alfa. Sunitinib also demonstrates efficacy for gastrointes-
tinal stromal tumors. A clinical trial was performed in 312 patients with
unresectable gastrointestinal stromal tumors after failure of imatinib therapy;
patients were randomized to receive either sunitinib or placebo [
76
]. Sunitinib
significantly increased the time to tumor progression by more than 20 weeks. The
first drug to simultaneously receive FDA approval for two different cancers,
sunitinib is now FDA-approved for metastatic renal cell carcinoma and imatinib-
resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor [
77
].
Sorafenib is another second-generation anti-angiogenic agent; this receptor
tyrosine kinase inhibitor blocks signaling through VEGF receptors, PDGF receptors,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search