Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
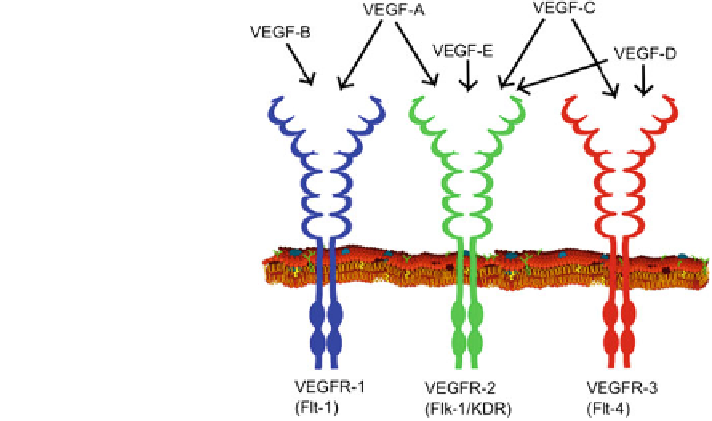
Fig. 2 VEGF isoforms and
receptors
promotes the transcription of genes encoding VEGF [
9
]. Upon translation and
secretion, VEGF binds to receptor tyrosine kinases (VEGF receptors, also called
VEGFR) located on the surfaces of neighboring endothelial cells [
10
]. Several
isoforms of VEGF exist that bind to a family of different VEGF receptors (Fig.
2
).
The binding of VEGF to its receptors activates blood vessel formation, increases
vascular permeability, and contributes to endothelial cell survival in blood vessels
[
11
]. VEGF signaling is absolutely required for embryonic development [
12
]. In
addition, upregulation of VEGF mRNA has been shown to occur during exercise
in humans [
13
]. At the same time, VEGF is the most significant and potent survival
factor in malignant tumor growth and metastasis [
14
].
Another important family of pro-angiogenic mediators is the fibroblast growth
factors (FGF) [
15
]; the fibroblast growth factor family comprises 22 polypeptides
that promote angiogenesis [
16
]. As with VEGF, the production and secretion of
FGF are stimulated by HIF during hypoxic conditions. Once secreted, FGF binds
to FGF receptors on endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and myoblasts. In
ischemic tissue, FGF4 induces endothelial cell proliferation, as well as the
secretion of metalloproteinases to carve out paths for new blood vessels [
17
].
FGF4 also stimulates secretion of VEGF, which subsequently stimulates angio-
genesis. Moreover, it has recently been demonstrated that FGF9 orchestrates the
wrapping of smooth muscle cells around nascent blood vessels during angiogen-
esis, to produce durable vasoresponsive blood vessels [
18
]. Other endogenous
pro-angiogenic molecules include platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF),
granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GCSF), placental growth factor (PlGF),
angiopoietin, and angiogenin [
19
,
20
].
The actions of pro-angiogenic molecules are countered by anti-angiogenic, also
known as angiostatic, regulatory molecules. Endogenous anti-angiogenic molecules
include angiostatin and endostatin [
21
]. Angiostatin interferes with ATP production,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search