Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
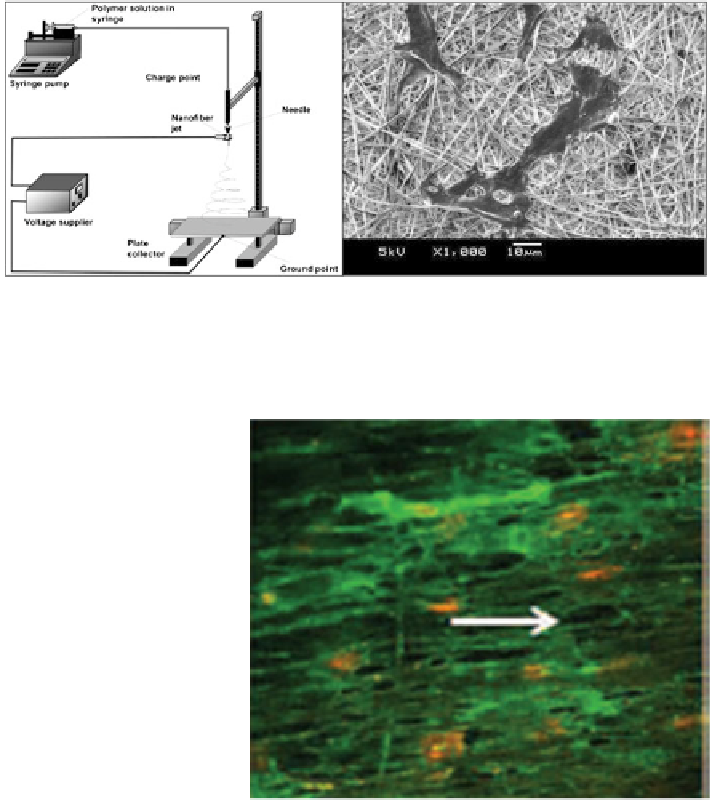
Fig. 4 Schematic of electrospinning apparatus setup. (Left image) The polymer solution is
pushed out through a syringe pump and then jetted out by an applied voltage. It is then collected
on a grounded plate. (Right image) SEM image of endothelial cells adhered onto P(LLA-CL)
nanofiber scaffold after 3 days of culture [
18
]
Fig. 5 Fluorescent image of
endothelial cells adhered onto
aligned P(LLA-CL) scaffold.
The endothelial cells were
cultured for 3 days and
stained for platelet
endothelial cell adhesion
molecule-1 (PECAM-1)
(green) and the nucleus
(red)[
19
]
Subsequent studies used fibrous scaffolds to guide the growth direction of
engineered blood vessels. In one study, the endothelial cells and smooth muscle
cells were seeded onto an electrospun poly(L-lactic acid)-co-poly(e-caprolactone)
nanofiber scaffold. The scaffold facilitated the adhesion of endothelial cells and
smooth muscle cells, and further supported their natural phenotypes in vitro. The
smooth muscle cells displayed the classic spindle shape and the endothelial cells
displayed a cobblestone morphology. Furthermore, both the endothelial cells and
smooth muscle cells migrated through the pores of the scaffold [
18
].
These microfiber surfaces were further coated with collagen in order to emulate
the microstructure of artery walls more closely. Endothelial cells grew along the
aligned nanofibers and also stimulated the smooth muscle cells to exhibit a spindle
phenotype in vitro [
19
]. However, despite these impressive cell alignments on the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search