Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
10000
Y-27632
8000
10000
10000
6000
Control
Y-27632
9500
9500
9000
4000
8500
8500
8000
8000
2000
uur
uur
0
1.0
1.5
2.0
0.5
Time (hr)
Fig. 2 Endothelial micromotion is Rho kinase-dependent. Impedance analysis of confluent
endothelial monolayers upon addition the Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (10 lM). Cells were
inoculated into electrode-containing wells and allowed to develop into confluent layers for 72 h.
At the time indicated by the arrow, the Y-27632 was added, and the resultant changes in
impedance were followed. Data were collected every second. Note that both the micromotion
(biological 'noise') decreases upon addition Y-27632
Much attention has been given to the regulation of AJs and their pivotal protein
VE-cadherin, a membrane spanning protein that forms homotypic interactions
between adjacent endothelial cells. The intracellular part of VE-cadherin is con-
nected to the F-actin cytoskeleton via both a-and b-catenin. In addition, a third
catenin, p120catenin (p120ctn), binds to VE-cadherin. P120ctn binding to
VE-cadherin is an important step in the regulation of AJ stabilisation as well as in
Rho GTPase regulation. Rac1 and Cdc42 are activated at sites where junctional
complexes are formed, while RhoA activity is downregulated when the monolayer
reaches confluence. Furthermore, many GTPase regulator activities are directly
initiated by cadherin engagement [
22
,
23
]. Thus, a precise spatial and temporal
fine-tuning of the activity of Rho family GTPases is critically important in the
establishment and maintenance of junctions.








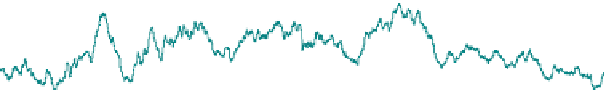

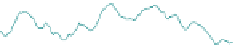





































Search WWH ::

Custom Search