Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1.0'
0.0'
0.5'
1.0'
2.5'
2.5'
1.5'
2.0'
4.0'
4.0'
5.5'
5.5'
Fig. 1 Spontaneous closure of inter-endothelial gaps. Differential interference contrast (DIC)
time-lapse imaging shows the transient nature of spontaneous gaps in post-confluent endothelial
cells. For identification, outlines of individual endothelial cells are shown in the images at
the right
Micromotion can be detected by electrical cell impedance sensing or ECIS tech-
nology, and is reflected by the 'biological' noise or fluctuations in the impedance
signal [
17
,
18
]. As can be seen in Fig.
2
, micromotion of resting endothelial
monolayers (the noise) is largely dependent on activity of Rho kinase, a down-
stream target of RhoA signalling.
Thus, junction proteins play a critical role in controlling vascular integrity both
in developing and existing vessels. Among these, VE-cadherin is crucial for this
regulation for its capability to remodel the F-actin cytoskeleton via modifying the
function of small GTPases of the Rho family (see below) [
11
].
3.1 Regulation by Rho GTPases
Initial attention for Rho GTPases was drawn to RhoA activation and its role in cell
contraction and endothelial hyperpermeability [
9
,
10
,
19
] Afterwards, the focus
has moved to the role of Rac and Cdc42 in the assembly and stability of inter-
endothelial junctions [
14
,
20
]. More recently, we identified a role for RhoA and its
effector Rho kinase in barrier maintenance [
21
].











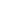
















Search WWH ::

Custom Search